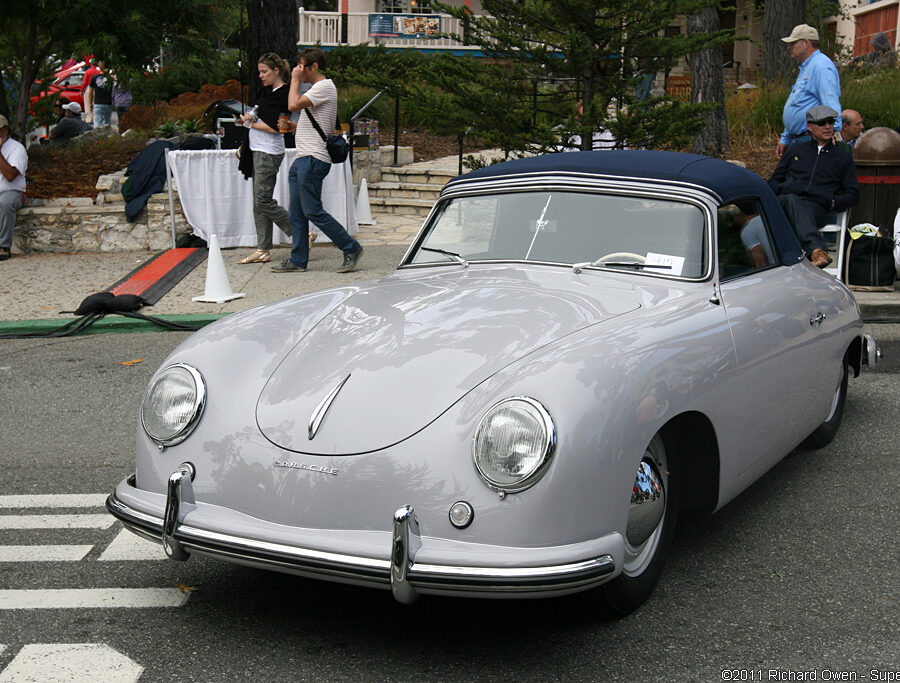
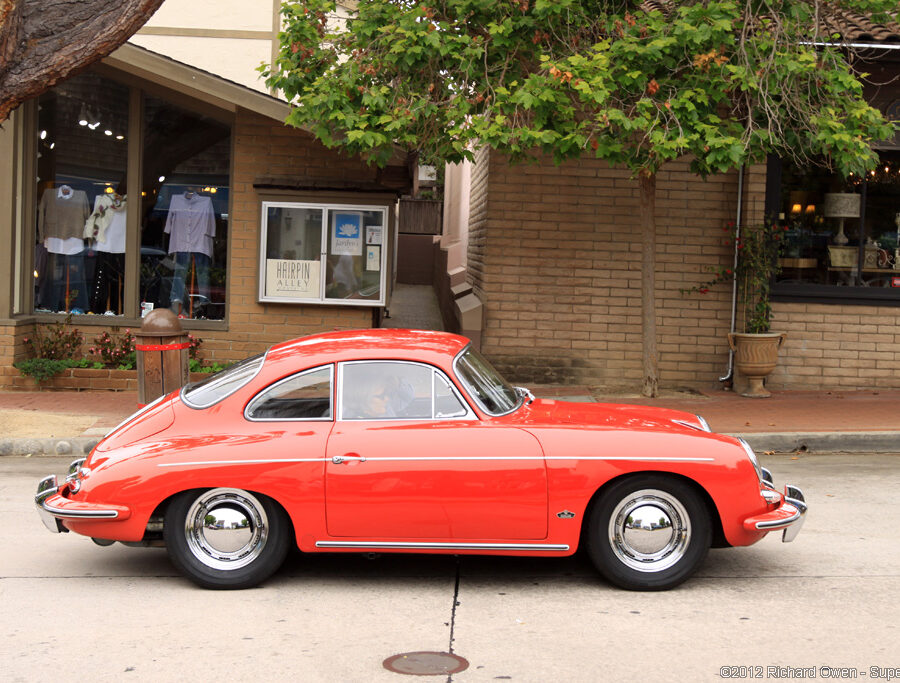
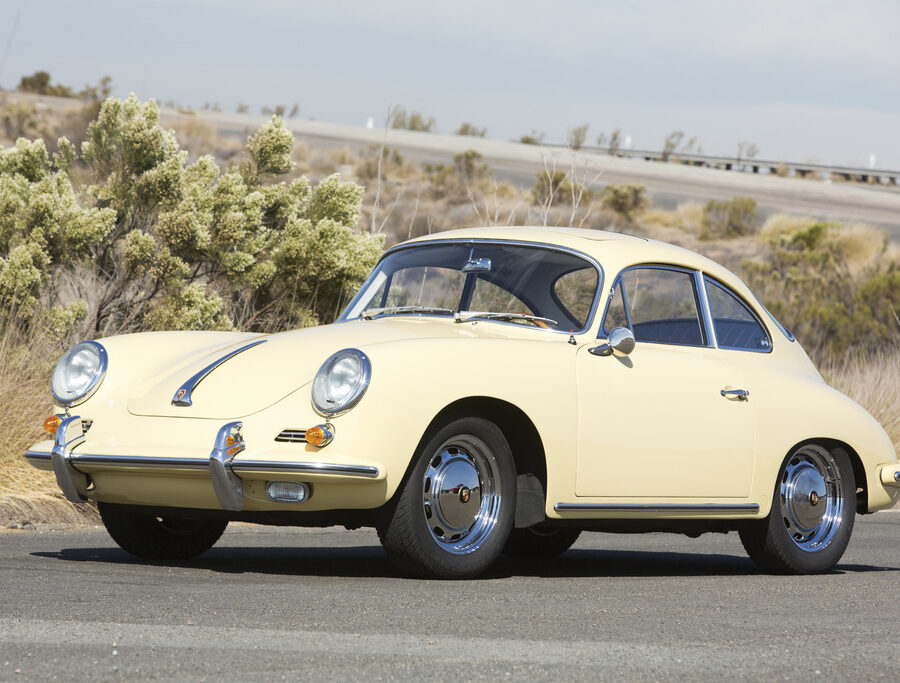
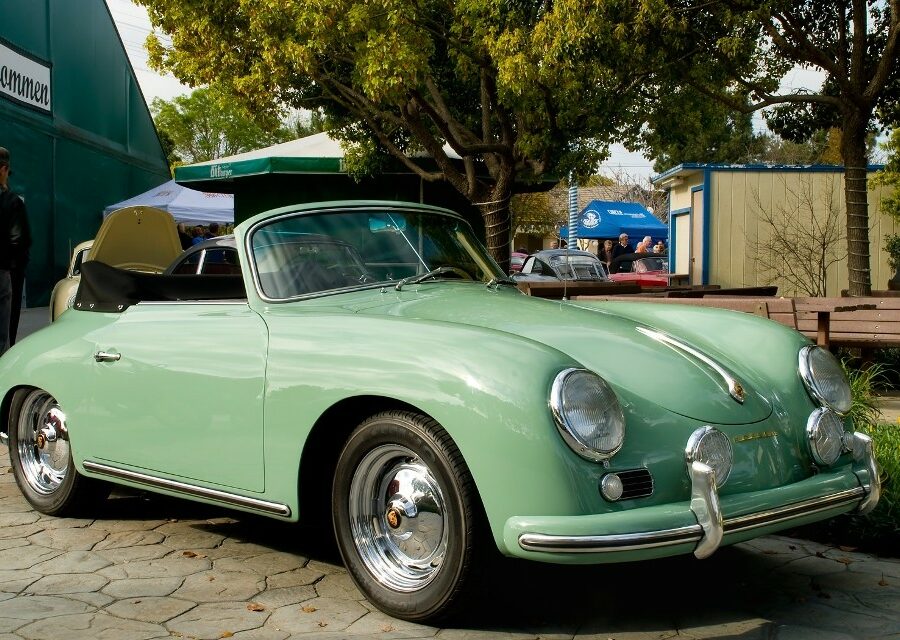
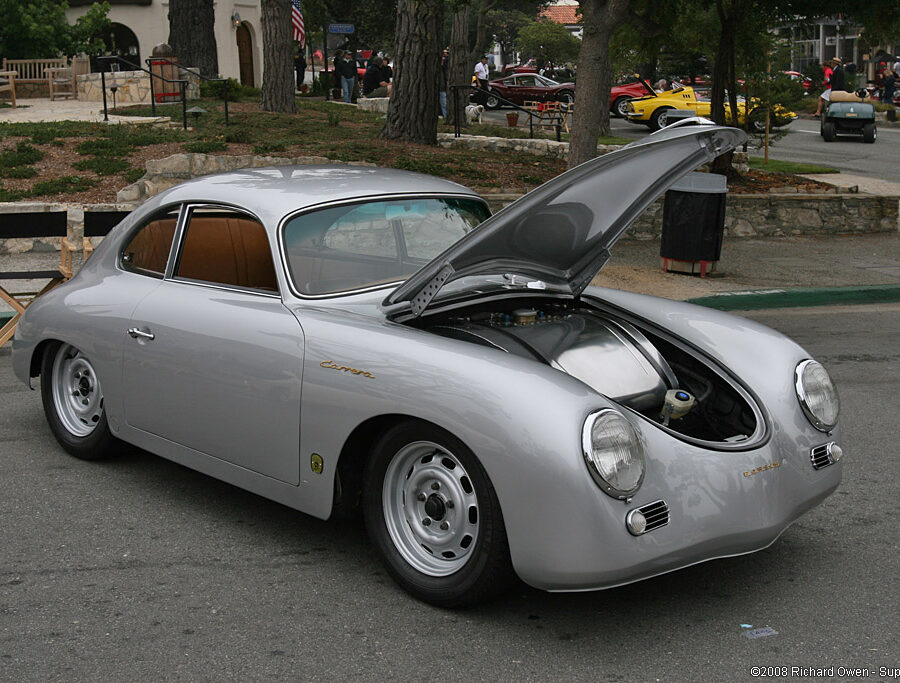
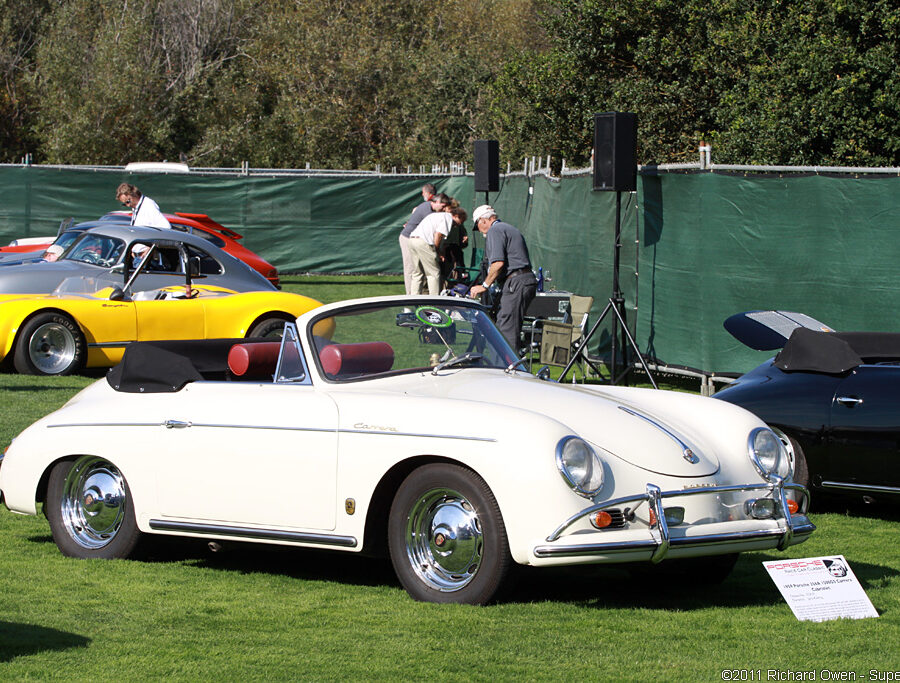
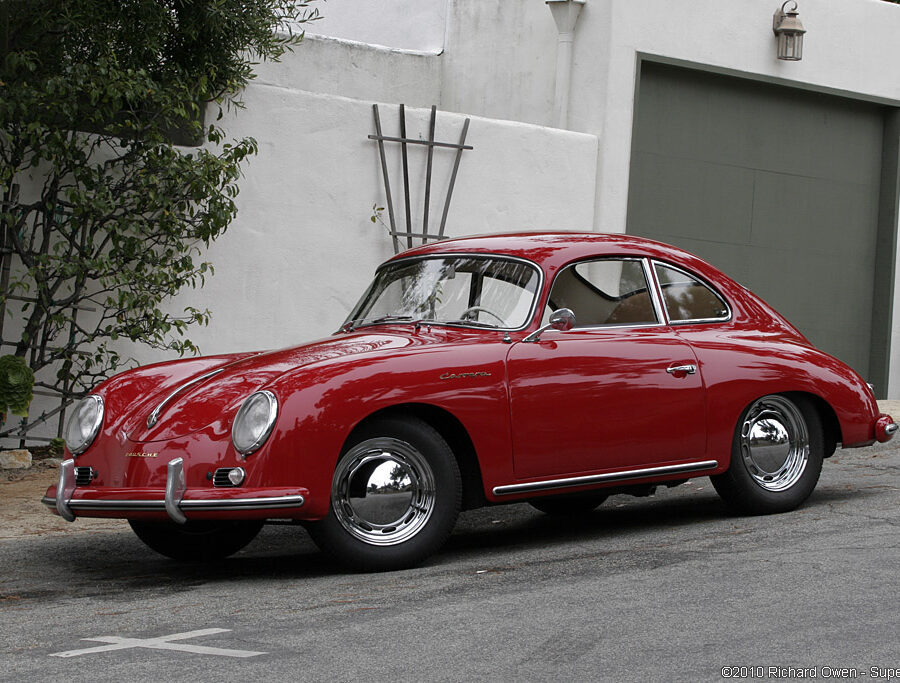
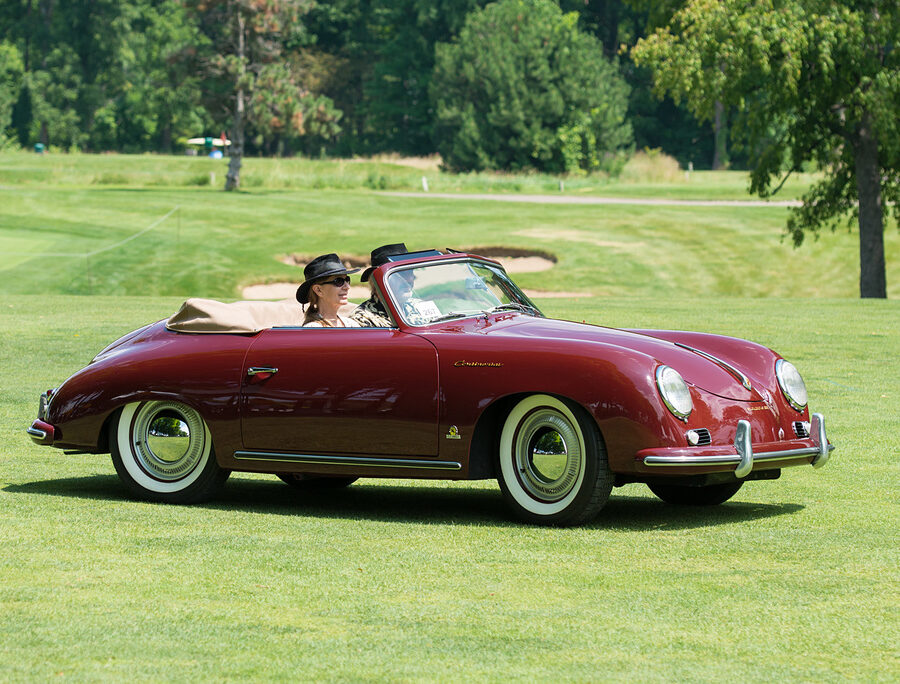
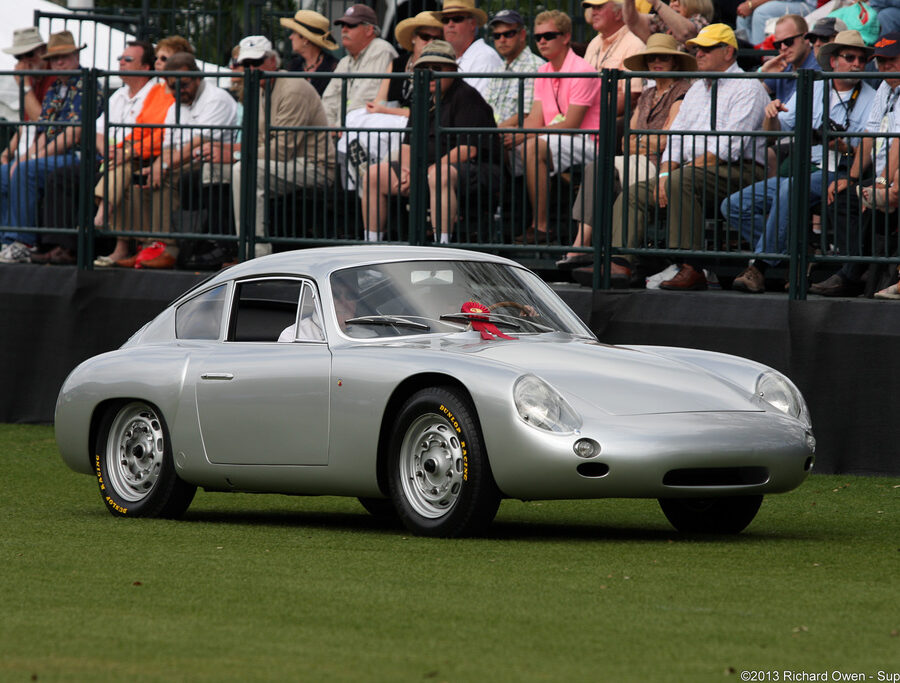
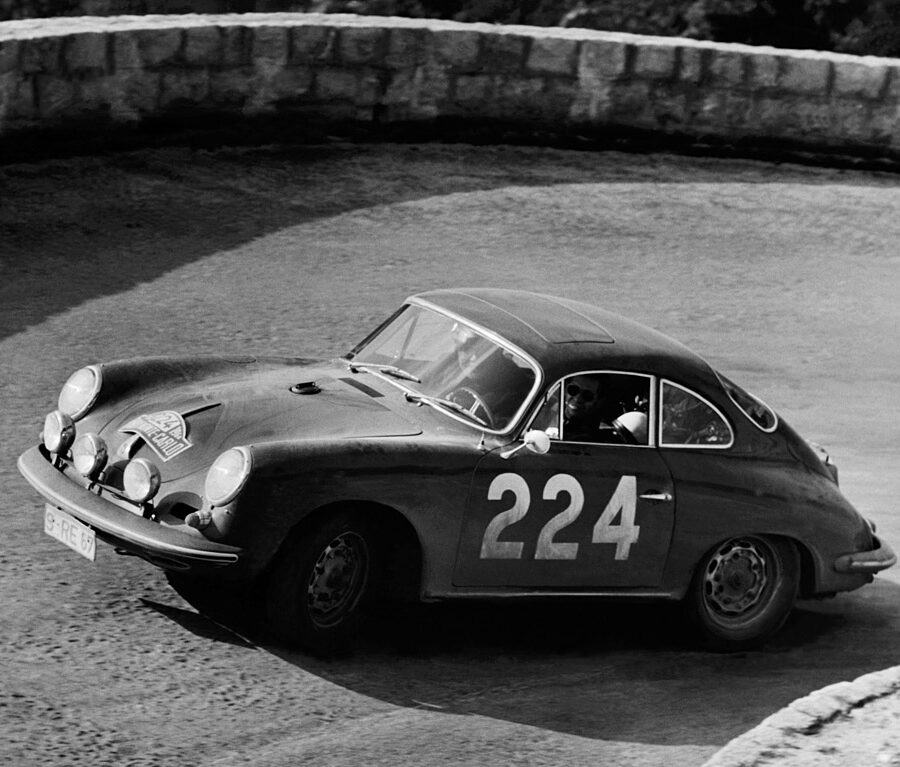
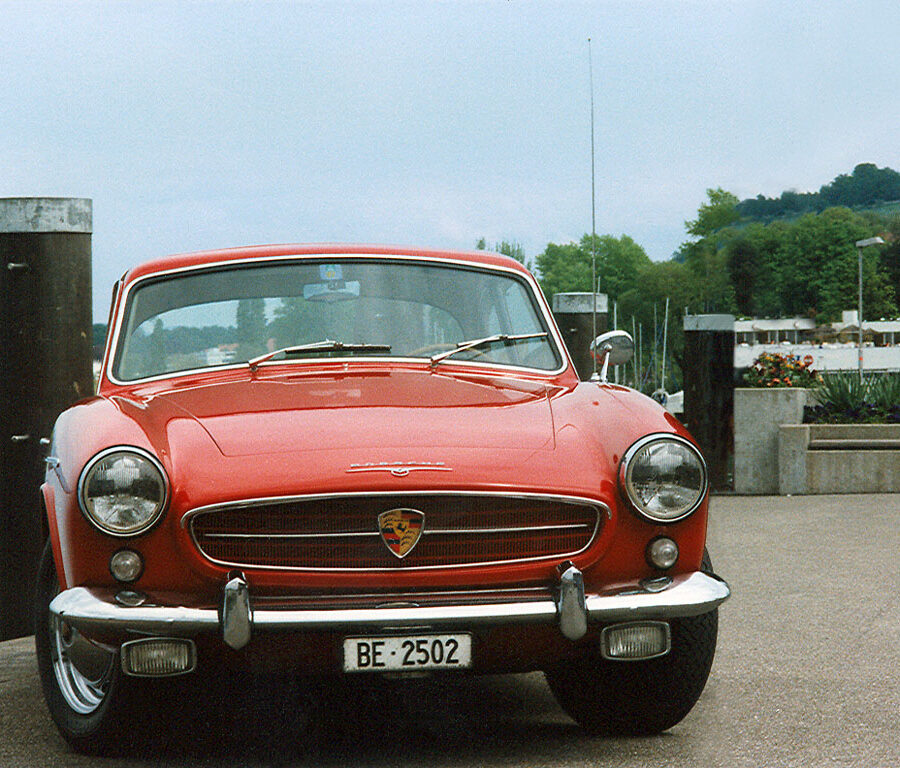
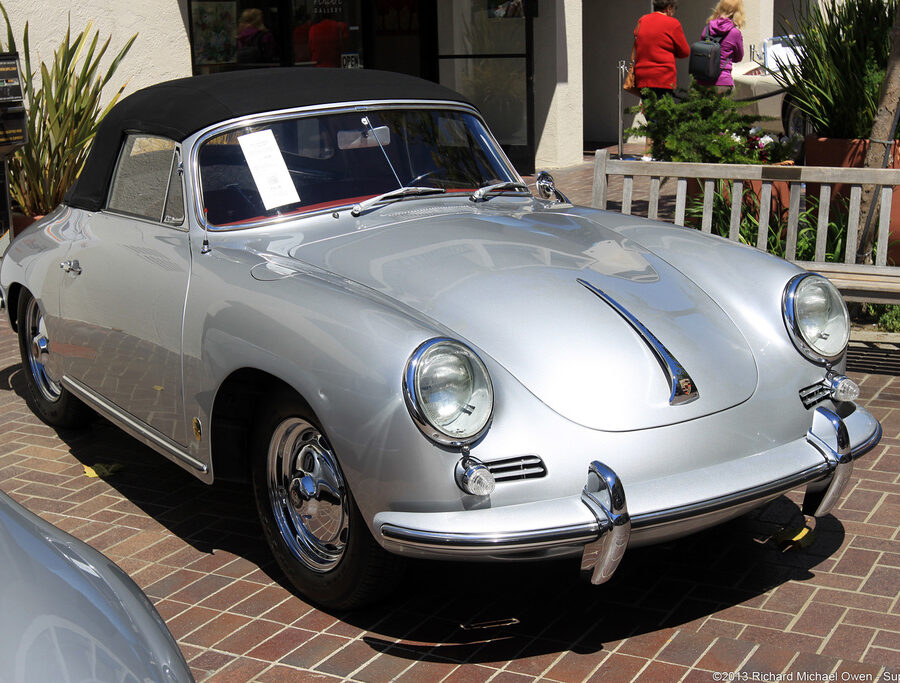
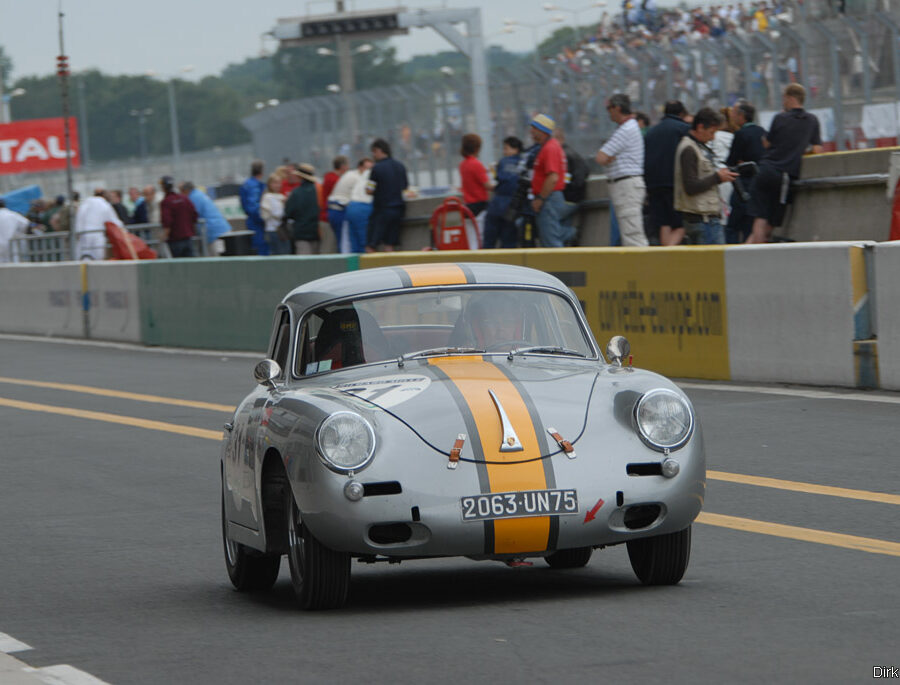
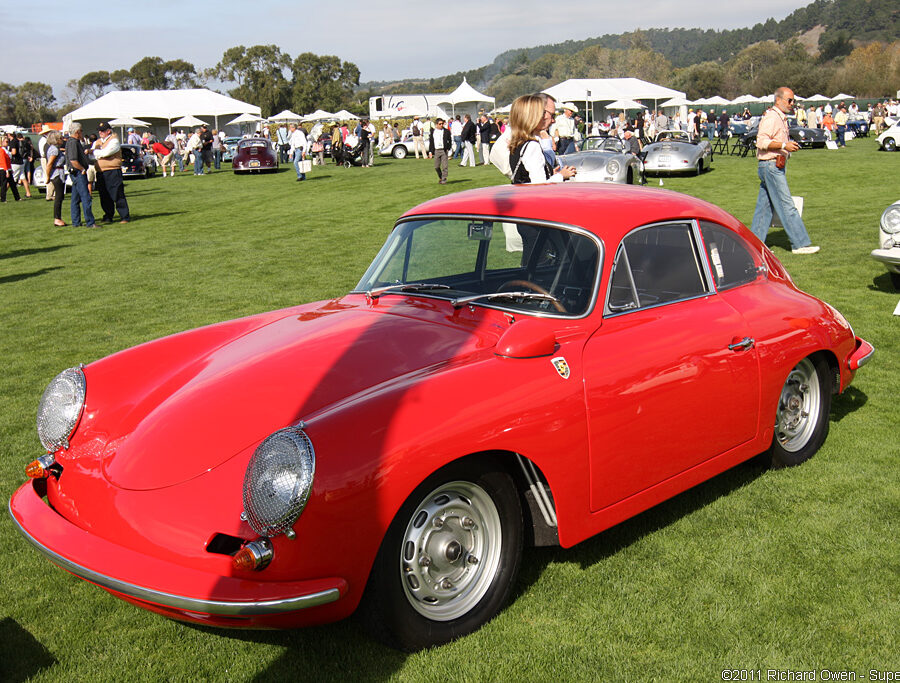
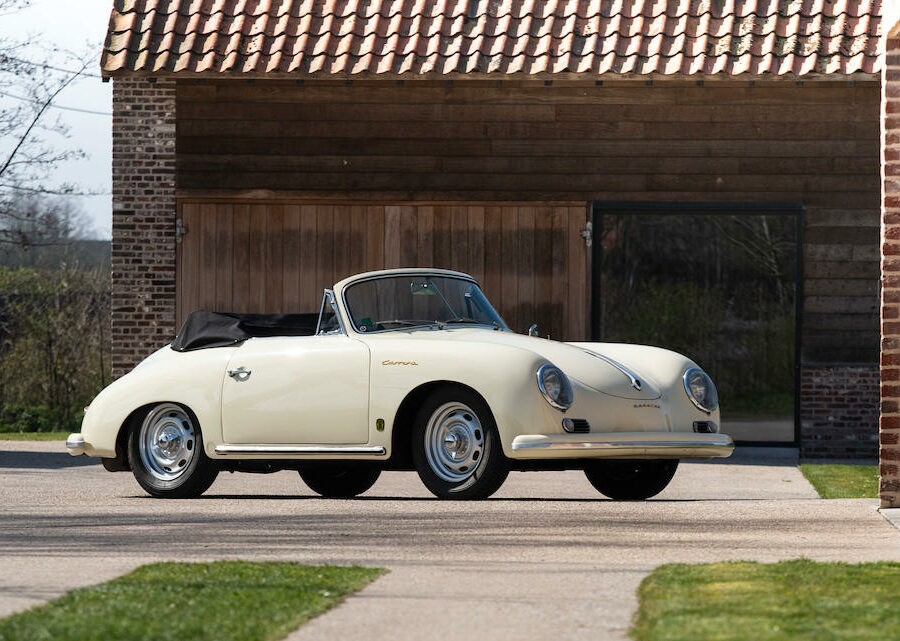
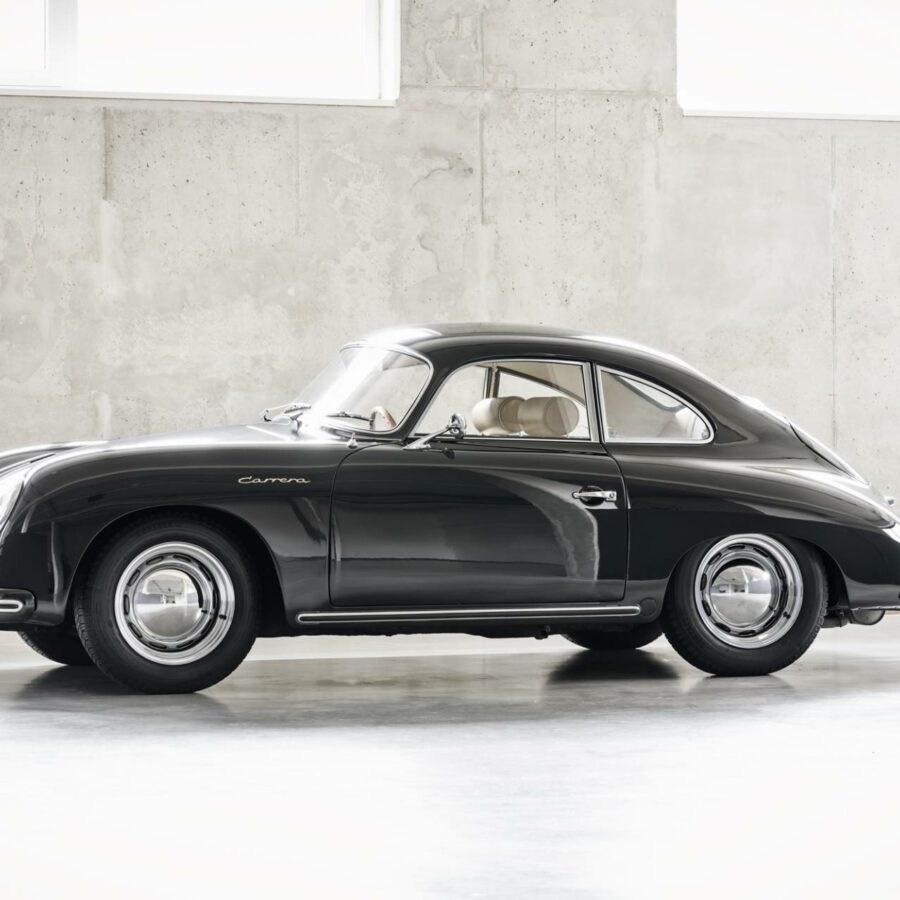
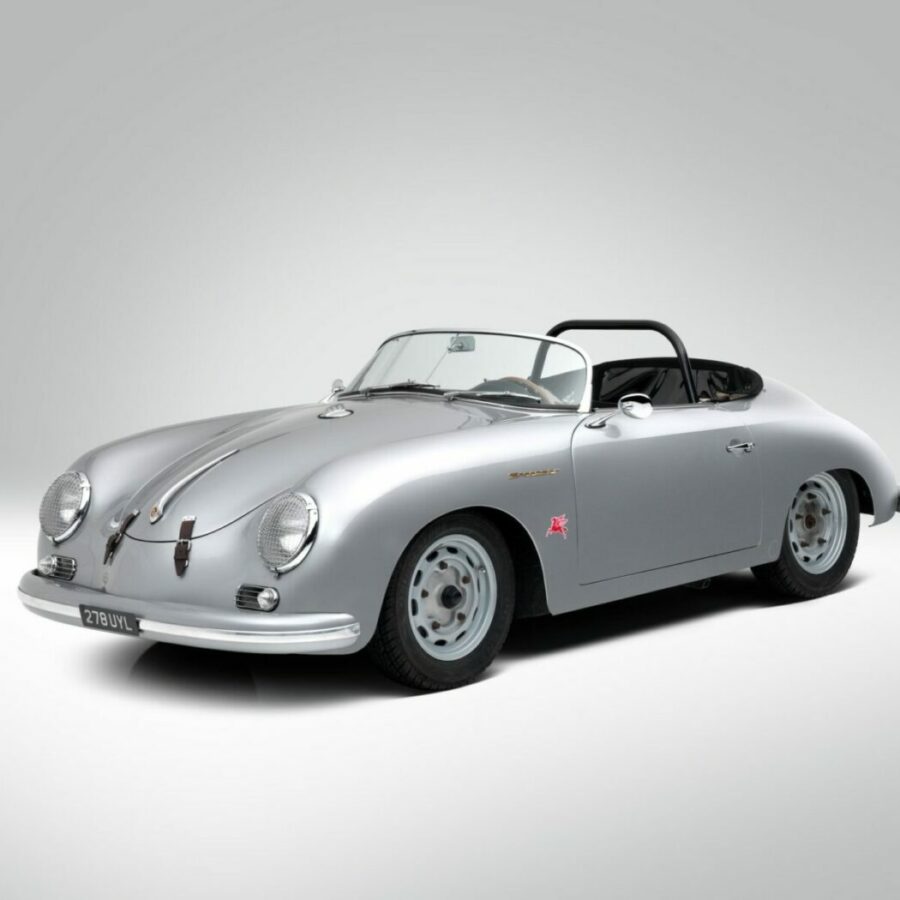
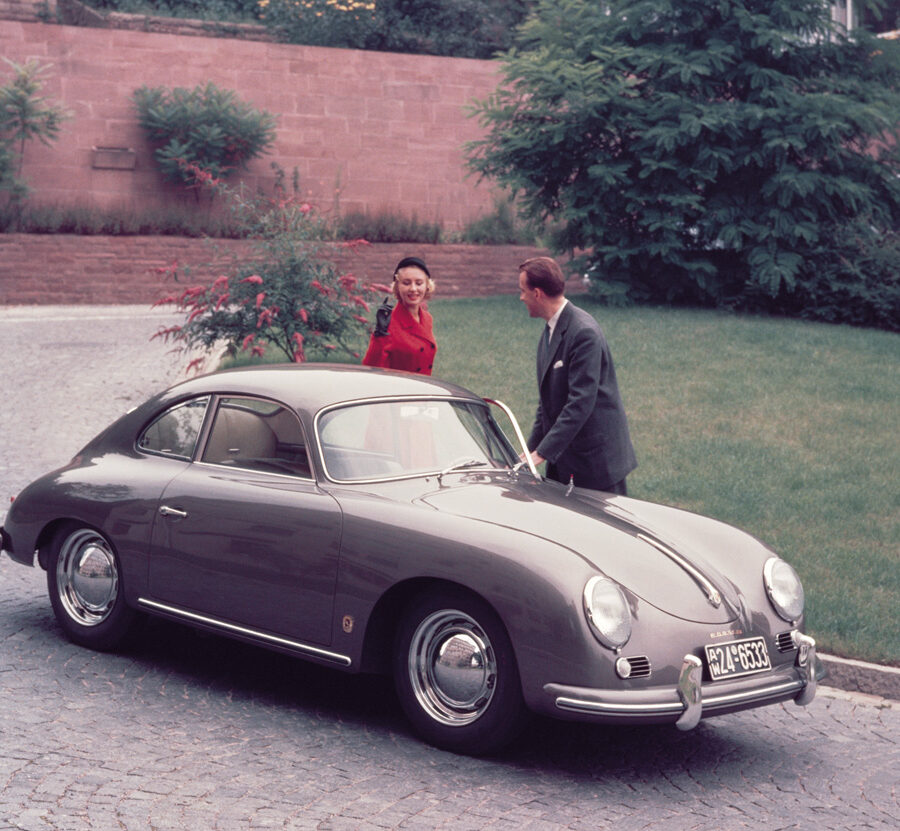
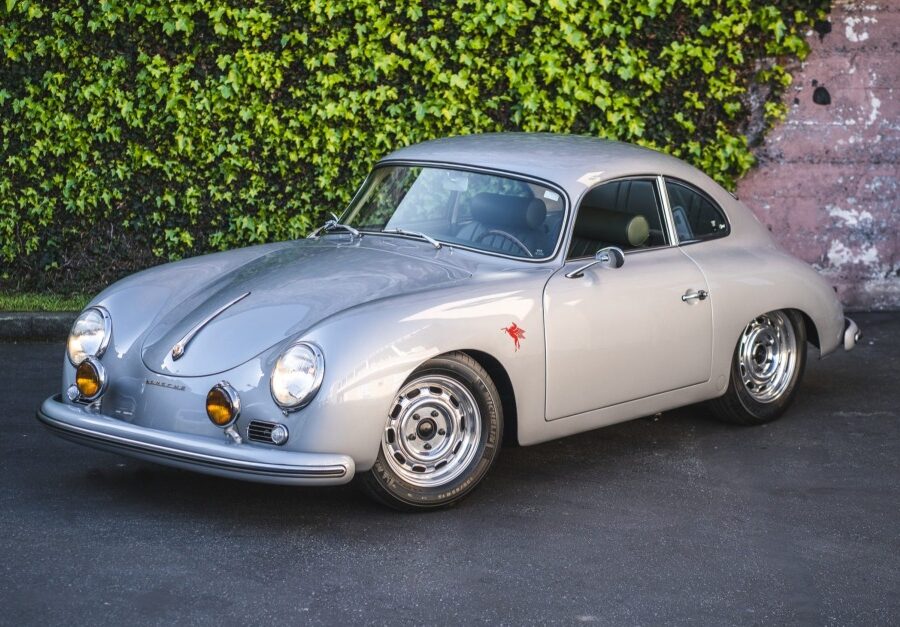
Porsche 356 C Carrera 2 (1964 – 1965)
The 130-horsepower Carrera 2000 GS was at the top of Porsche’s product line in 1964.
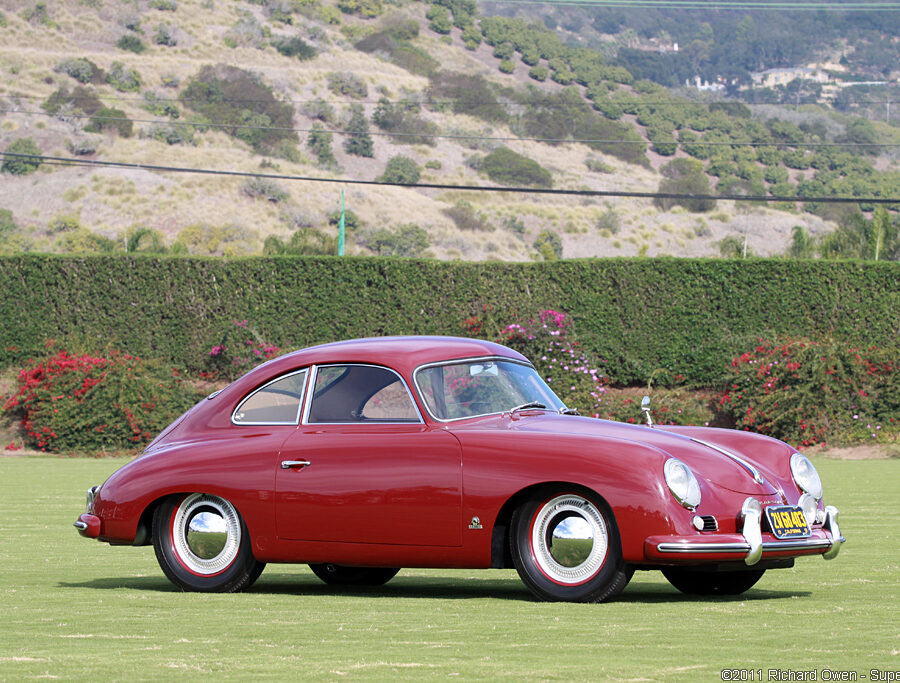
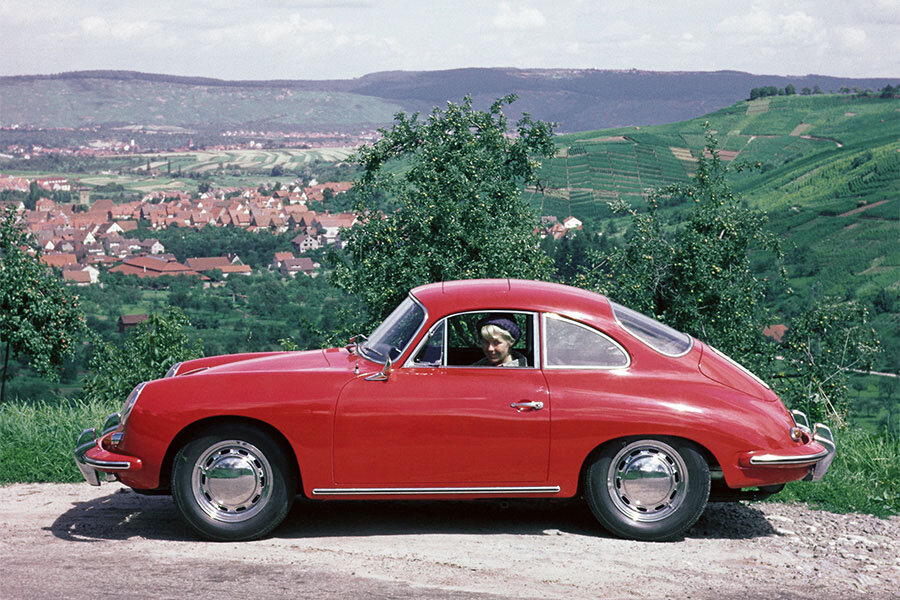
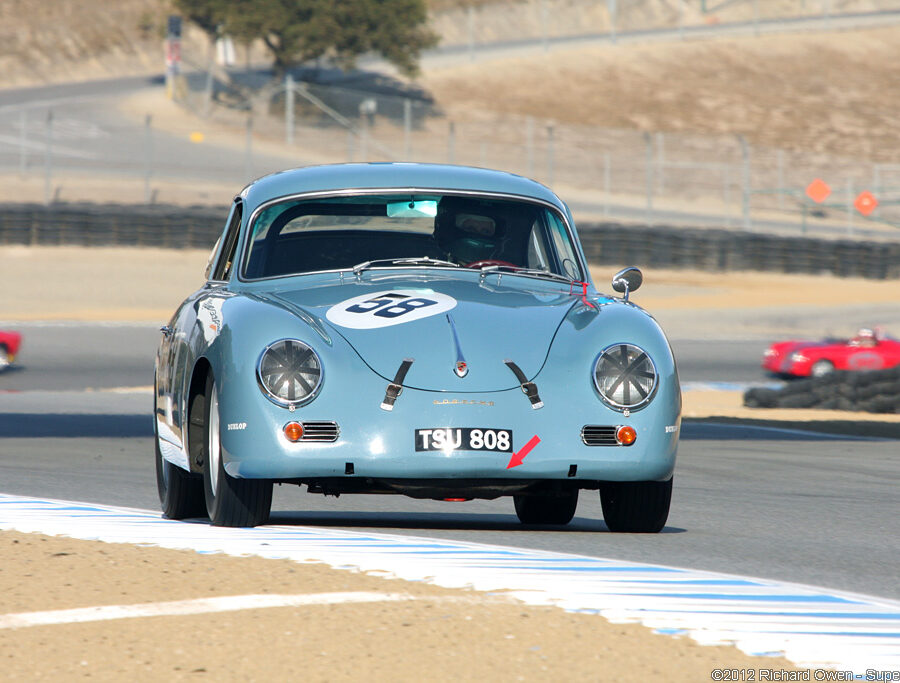
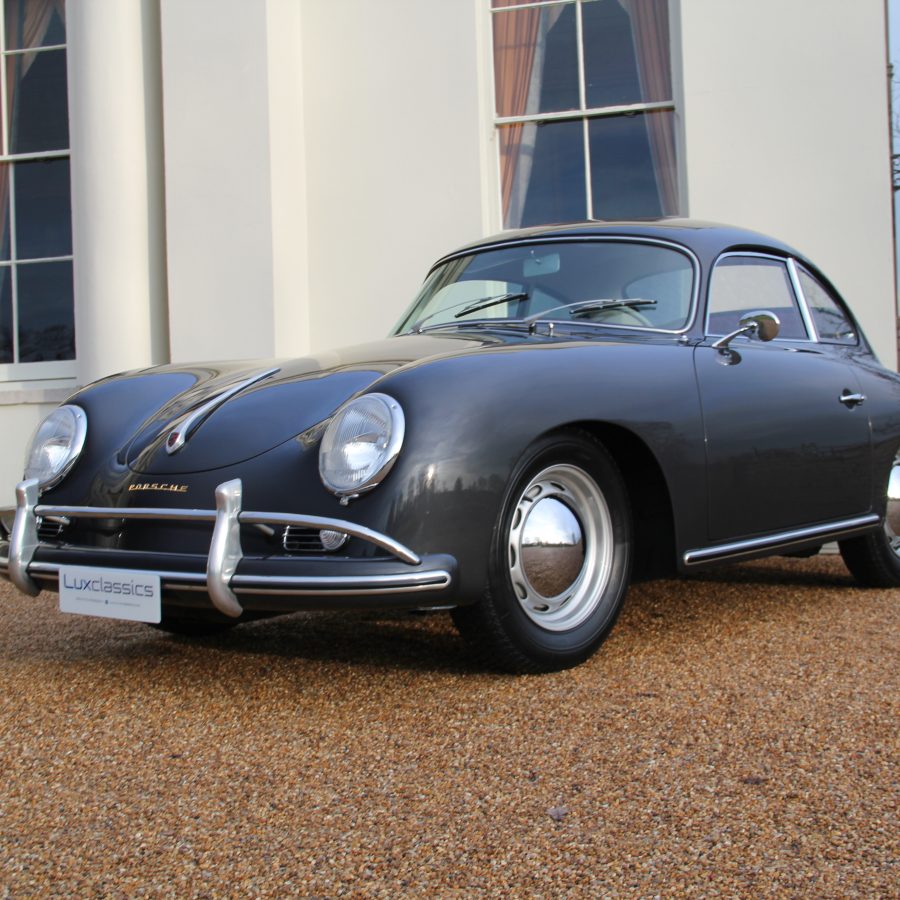
Porsche 356 C 1600 C (1964 – 1965)
The last revision of the 356 was the 356 C introduced for the 1964 model year. The base version was known as the 1600 C.
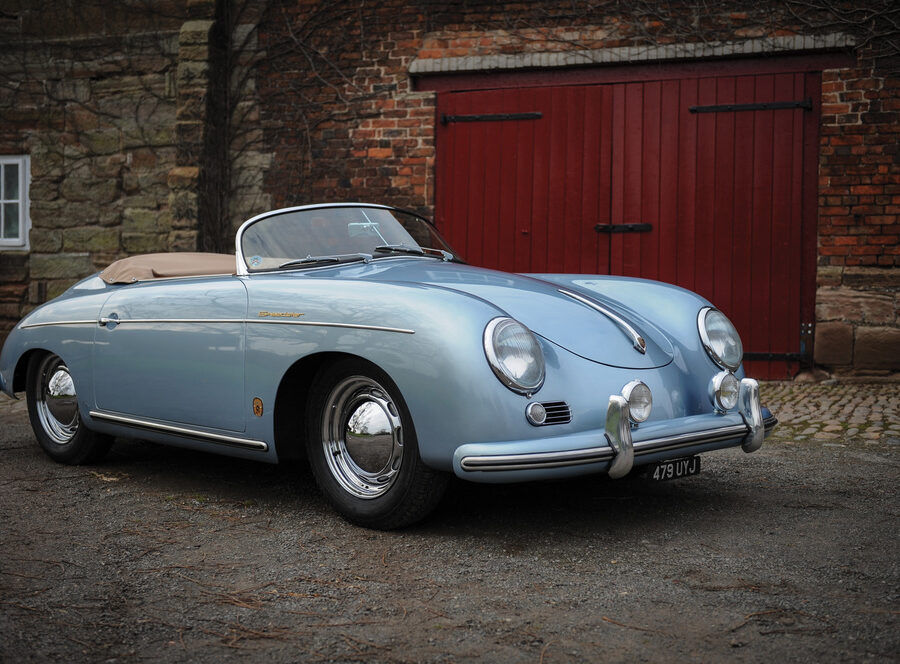
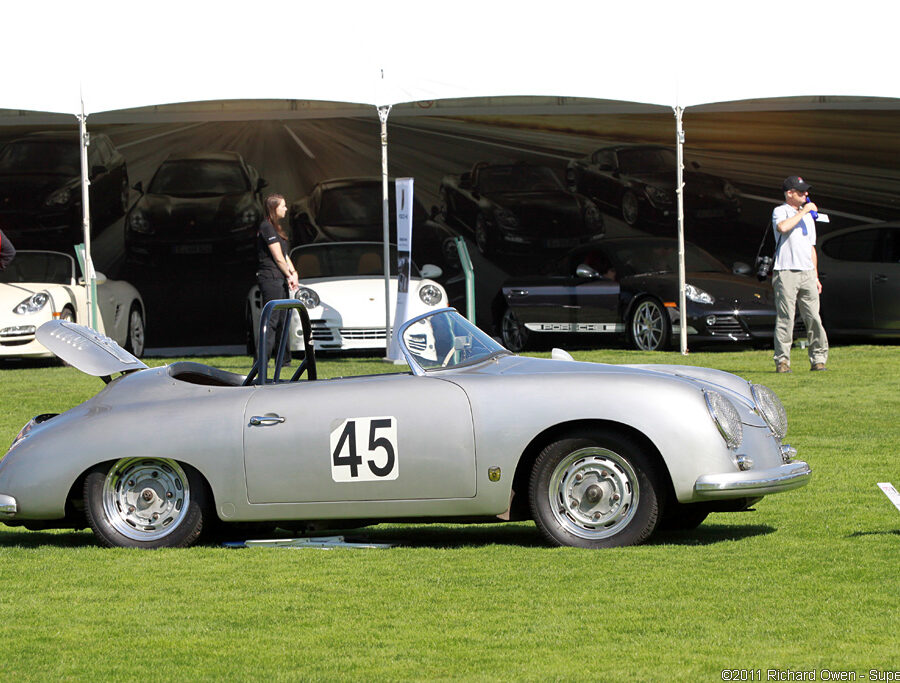
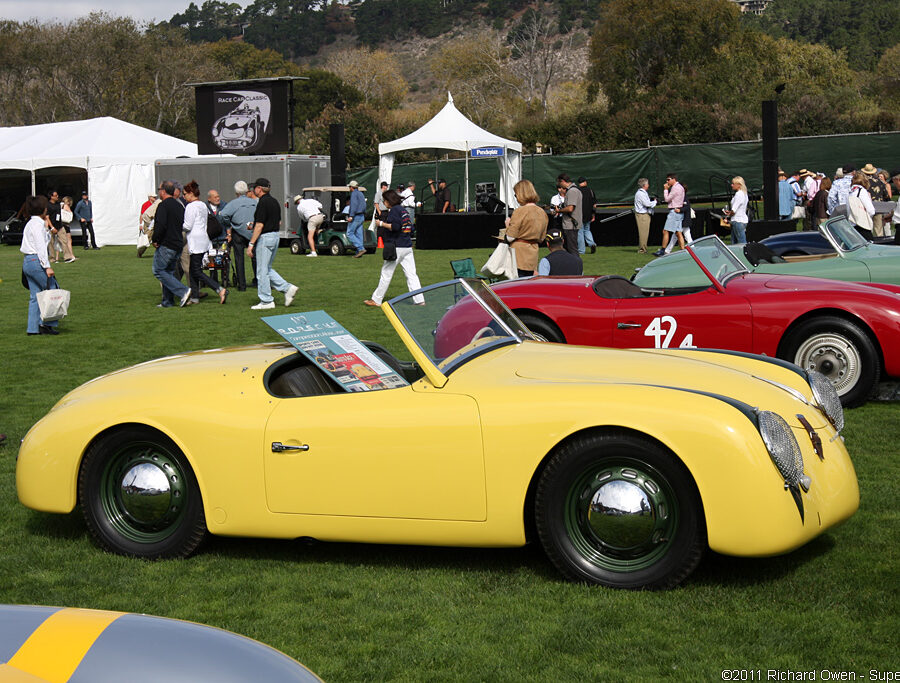
Porsche 356 A 1600 Zagato Speedster (1958)
The last project presented by the Milanese Atelier under the Zagato Classic program
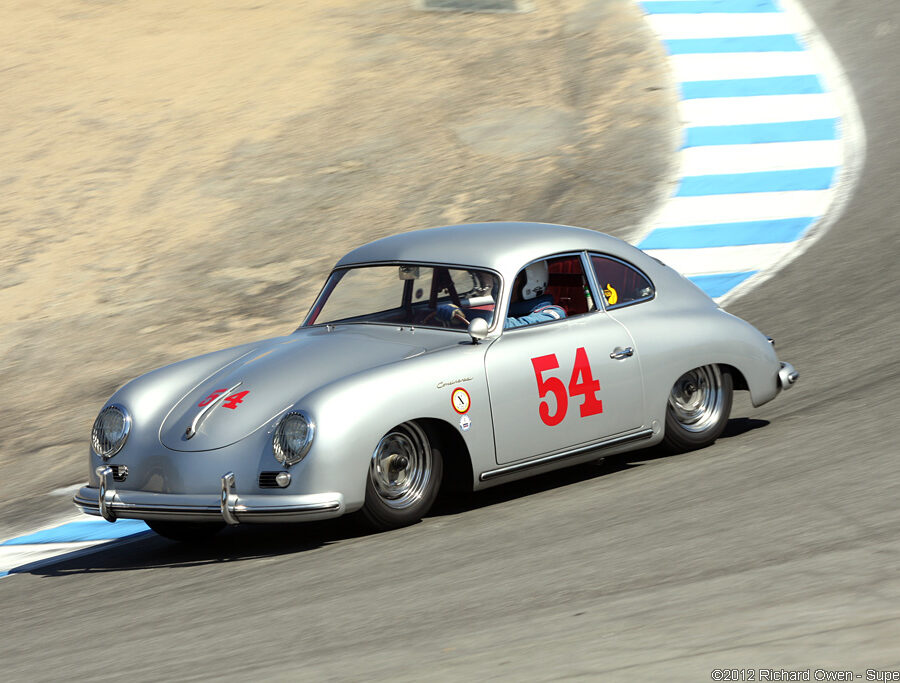
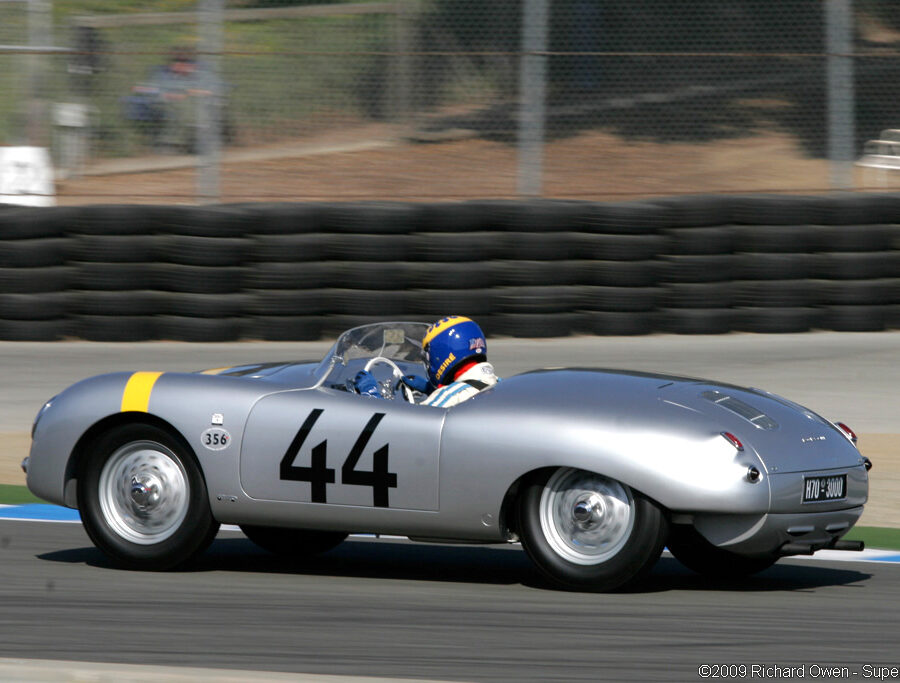
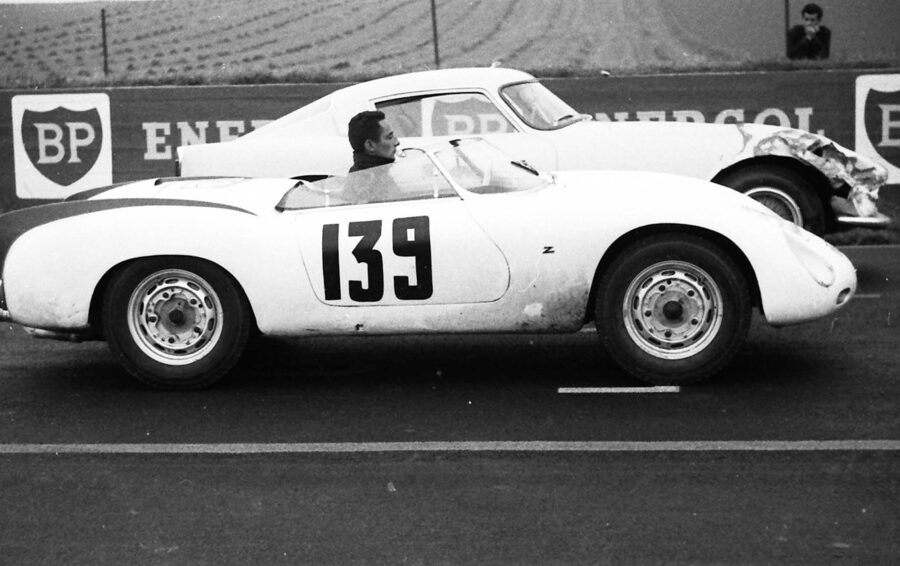
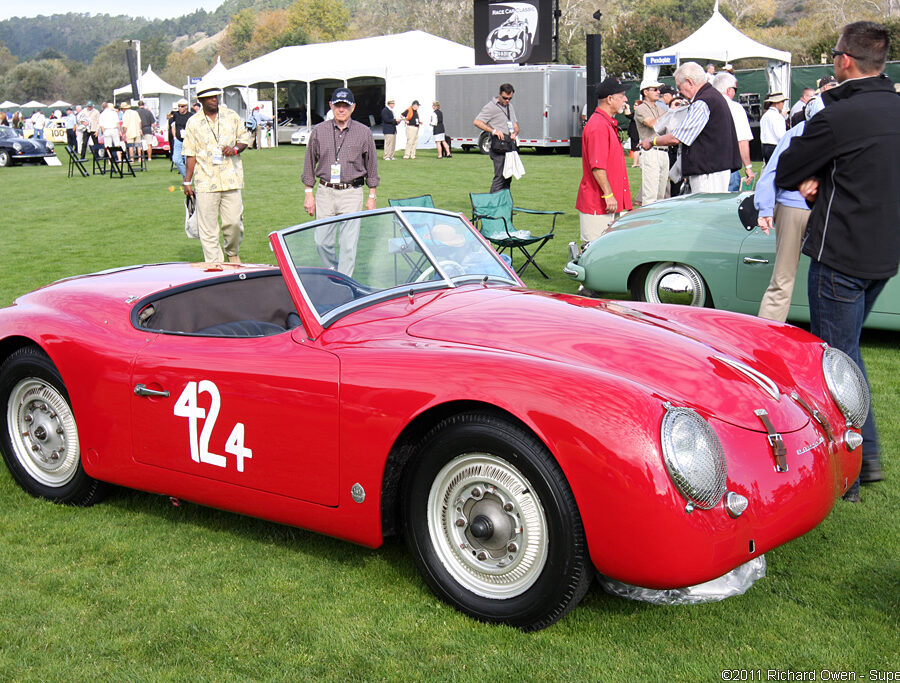
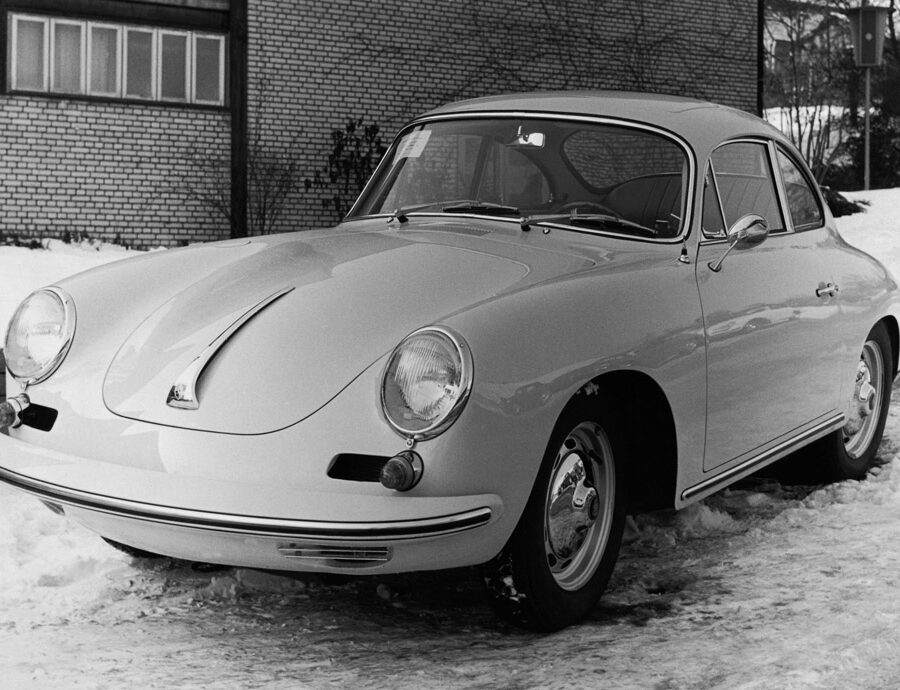
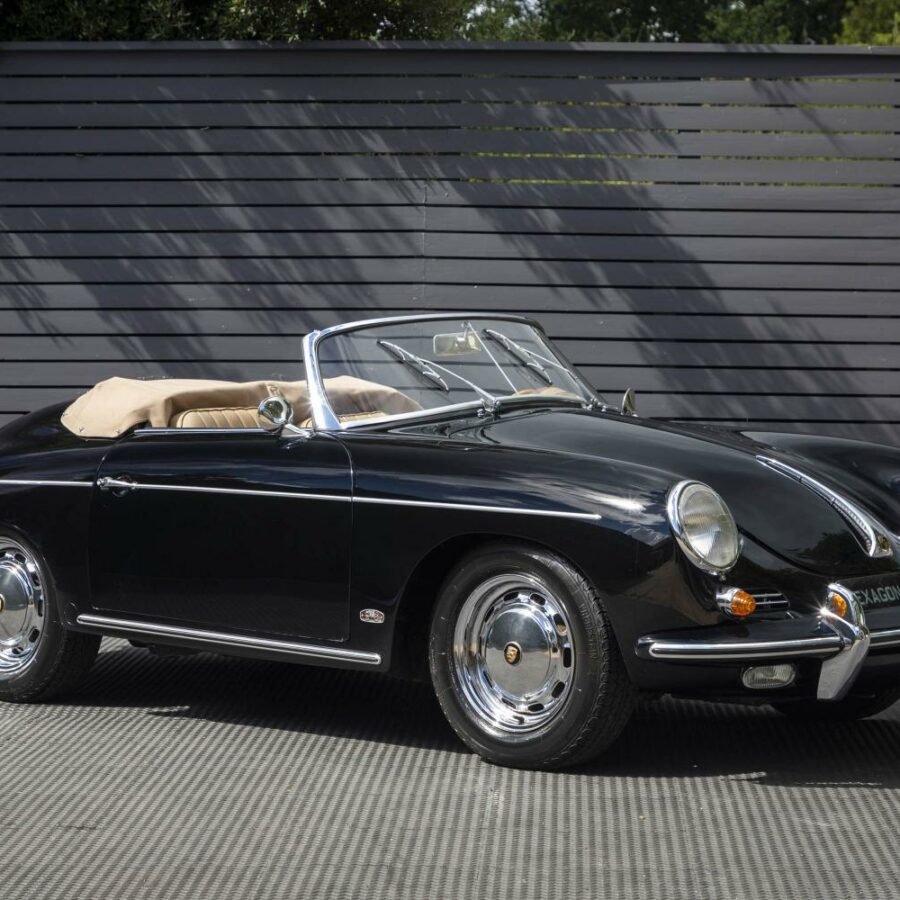
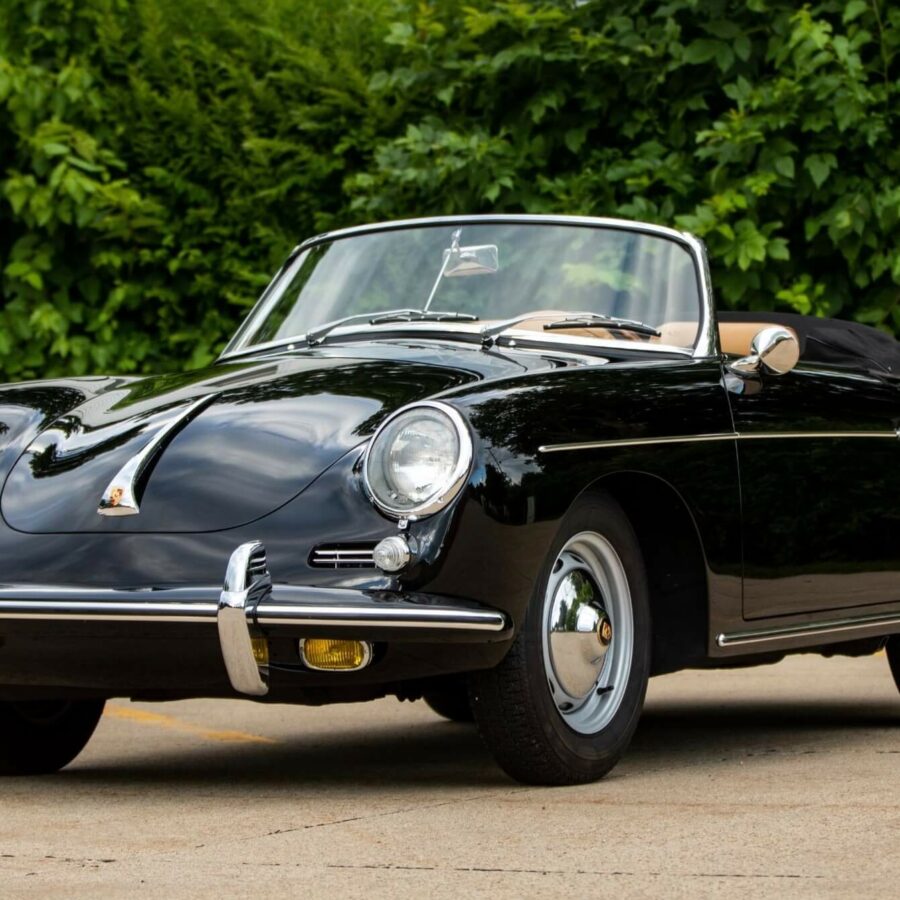
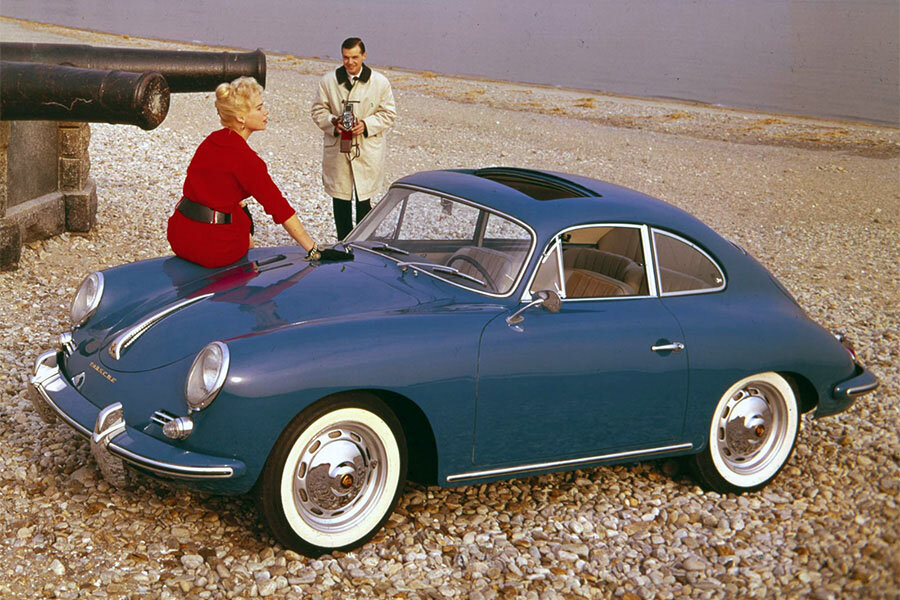
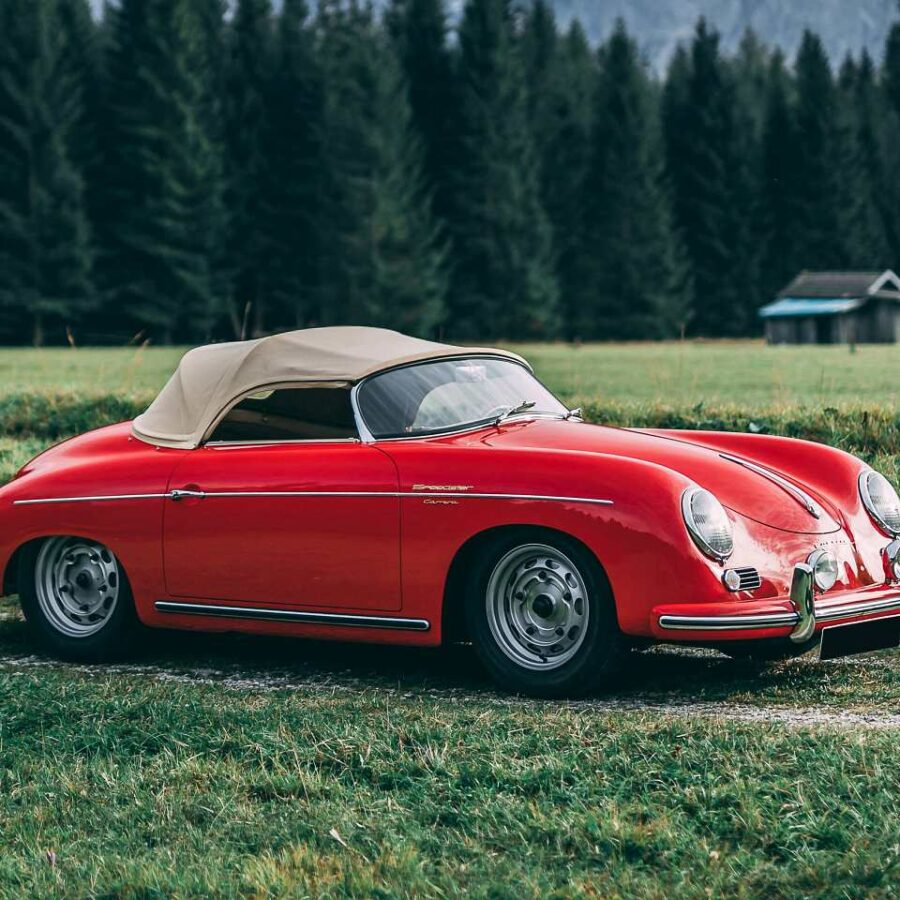
Porsche 356 B Carrera 2 (1962 – 1963)
The Carrera trailed a series of impressive 1.6 liter cars known as the 1600GS.
Porsche 356 B 1600 Super 90 (1959 – 1963)
New to the model was the Type 616/7 Super 90 engine which was an indirect replacement for the Carrera de Luxe models.
Porsche 356 B 1600 S (1959 – 1963)
The 1600 Super sat in the middle of the lineup, below the Super 90 and above the base 1600.
Porsche 356 B 1600 (1959 – 1963)
In 1959 Porsche revealed their updated 356, the 356B. Completely revised body that was more suitable for the American market.
Porsche 356 A 1500 Carrera GS (1956 – 1958)
Mated the potent four-camshaft engine from the 550 RS Spyder into the 356’s unassuming chassis.
Porsche 356 A 1600 S (1956 – 1959)
With the 356A came a larger 1582 cc engine that had higher compression to take advantage of the available higher octane fuels.
Porsche 356 A 1600 (1956 – 1959)
Released in September of 1955, the 356A/1600 came in cabriolet, coupe and speedster bodies from Reutter.
Porsche 356 A 1300 S (1956 – 1957)
The 1300 S got more power from its 1.3 Liter 8v Flat 4, at 60 bhp and more torque, now at 65 ft lbs.
Porsche 356 A 1300 (1956 – 1957)
44 hp, the naturally aspirated 1.3 Liter 8v Flat 4 gasoline engine
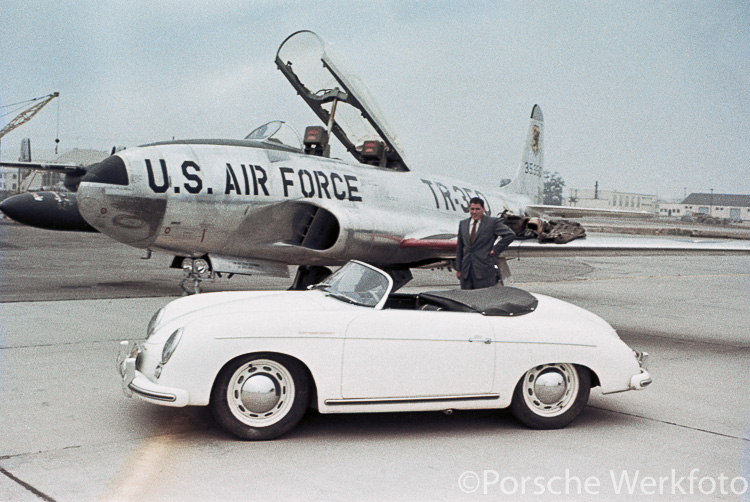
1952 Porsche 356 ‘America Roadster’
Max Hoffman convinced Porsche it needed a lightweight convertible to compete with Jaguar and Austin-Healey.
Porsche 356 1500 “Pre-A” Carrera (4-cam) (1955)
The 356 gets a race inspired 1500 cc four cam motor
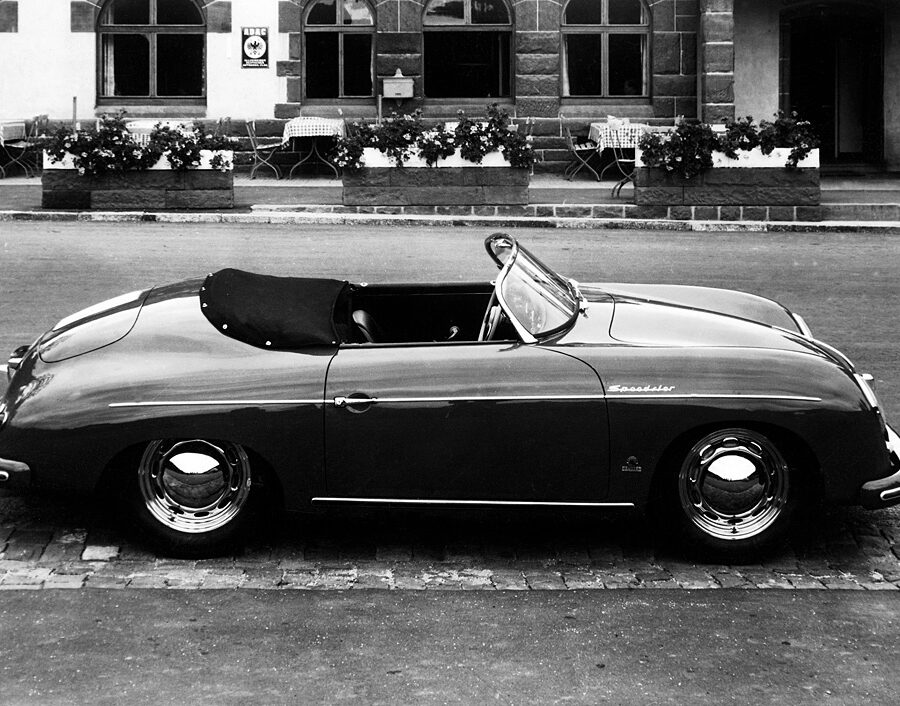
Porsche 356 1500 “Pre-A” Super Speedster (1955)
The ‘super’ version had more horsepower (70 vs the standard 60) and the powerful ‘type 528 engine’
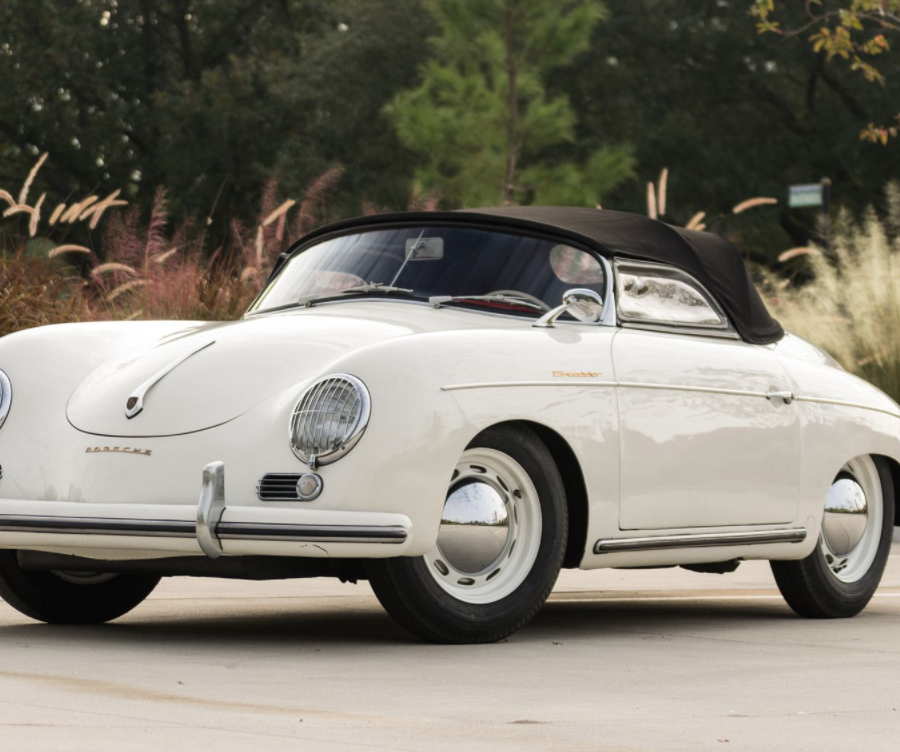
Porsche 356 1500 “Pre-A” Speedster (1954 – 1955)
Max Hoffmann convinced Porsche to built the 356 Speedster. A cheaper and more sporting alternative to the Coupe and Cab.
Porsche 356 1300 Super “Pre-A” (1954 – 1955)
In 1953, the 1300 S or "Super" was introduced, and the 1,100 cc engine was dropped.
Porsche 356 1500 Super “Pre-A” (1953 – 1955)
Porsche's competition department reworked the 1500 engine with hotter cams and bigger Carburetors, boosting power to 70 bhp.
Porsche 356 1500 “Pre-A” (1952 – 1955)
The 1500 was Porsche’s newest engine which was quickly fitted with 40 PIBC Solex carburetors
Porsche 356 1300 “Pre-A” (1951 – 1955)
In 1951, a bigger 1.3-litre Type 506 engine was announced. It marked the first significant move away from the original Volkswagen unit.
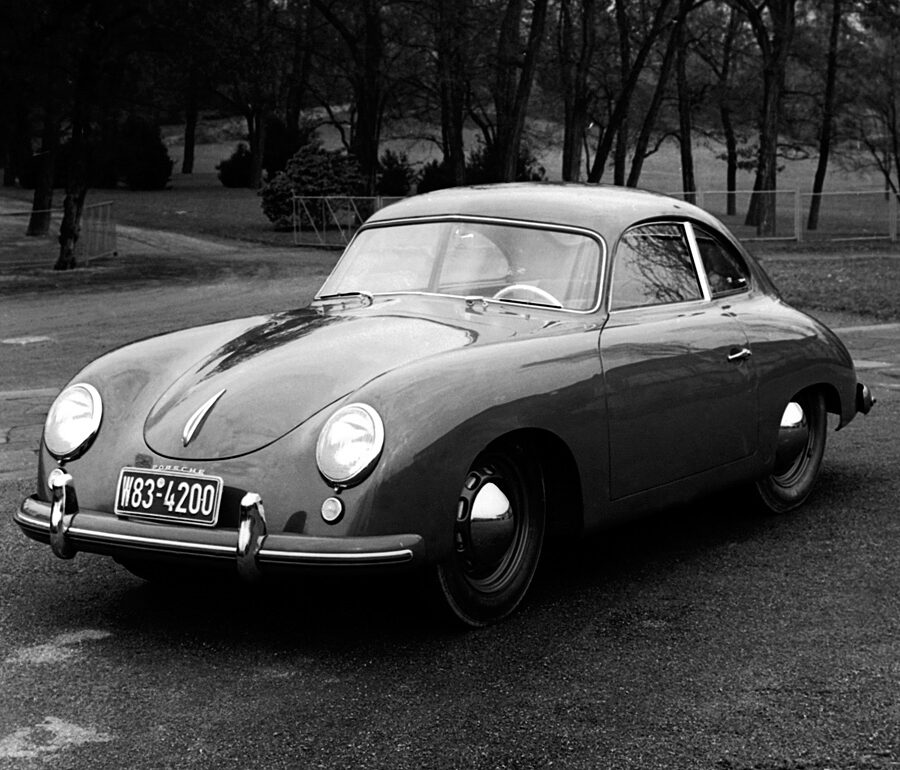
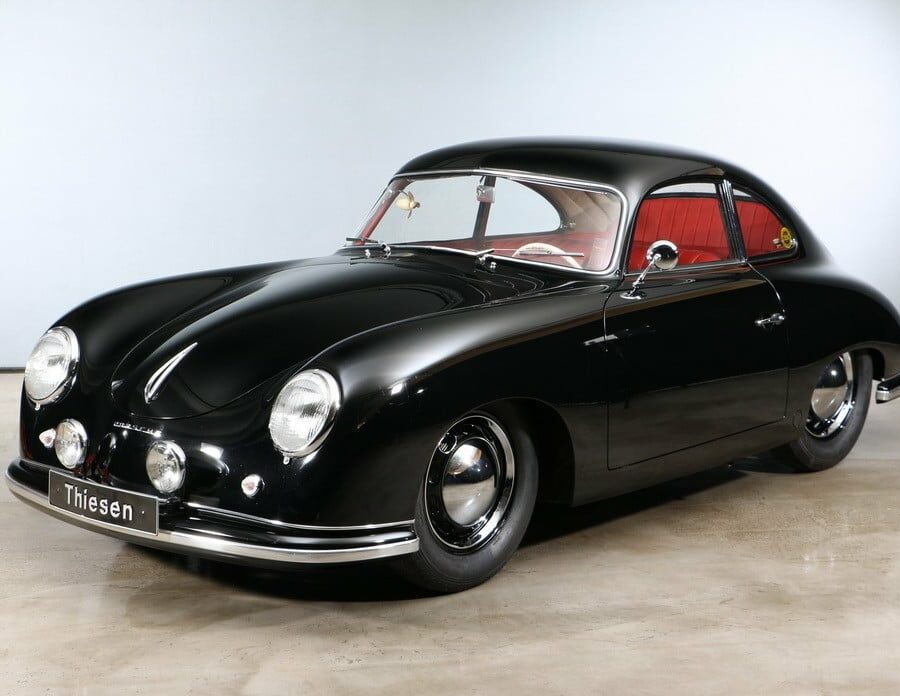
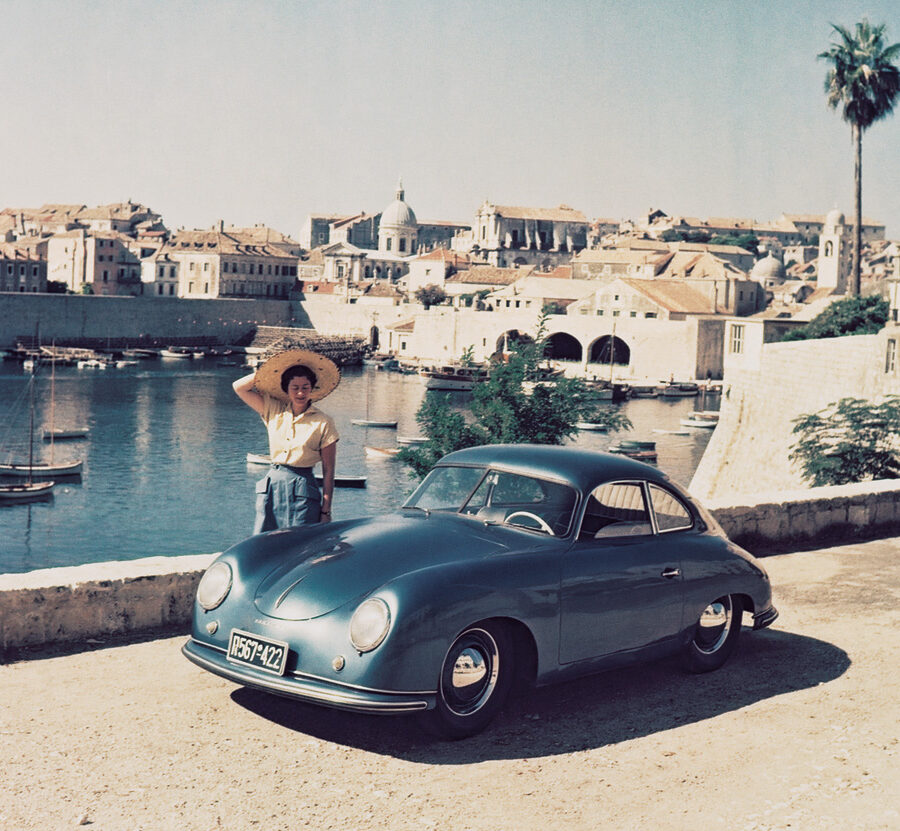
Porsche 356 1100 “Pre-A” (1950 – 1954)
The first Stuttgart-built 356 have later been called as 356 Pre-A.
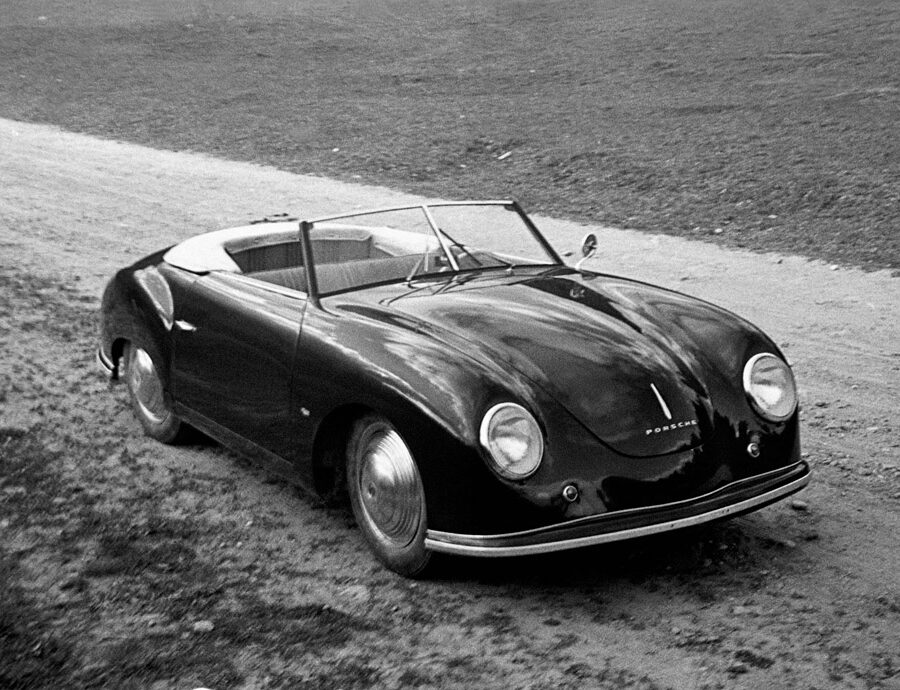
Porsche 356/2 “Gmünd” Cabriolet (1948 – 1951)
Of the 52 cars made in Gmünd, only eight were built up as cabriolets.