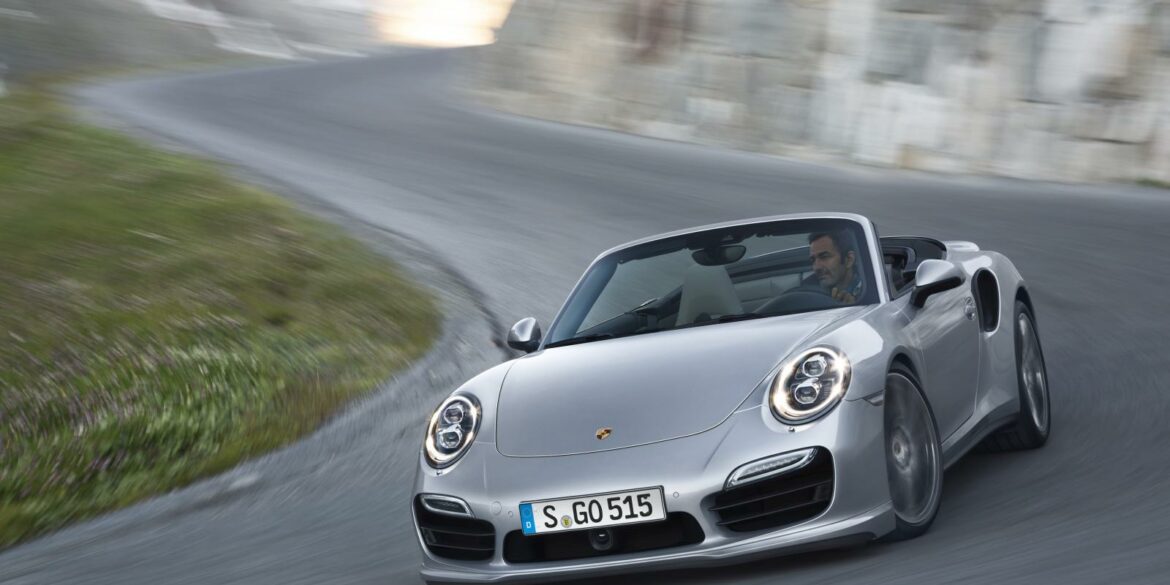
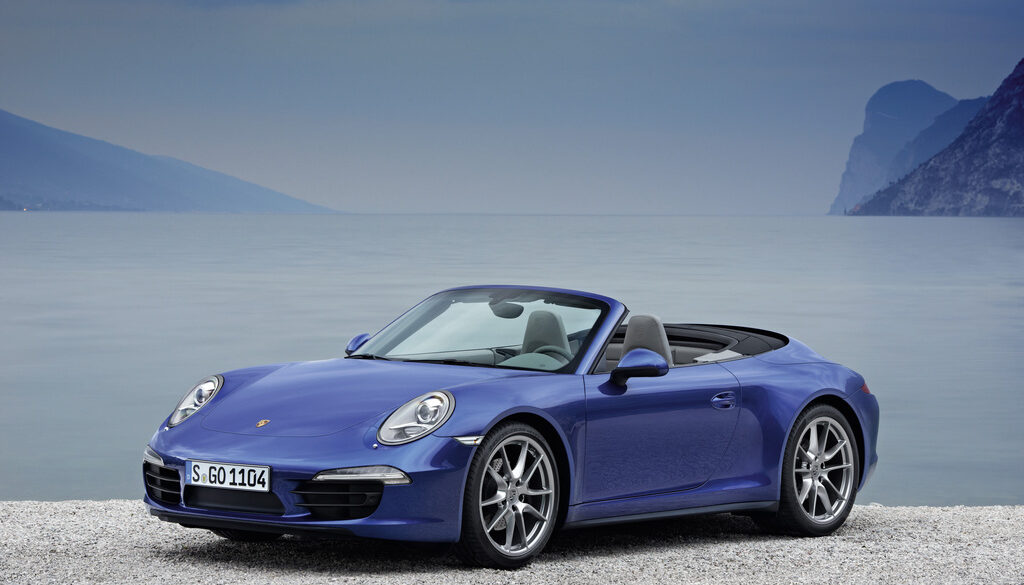
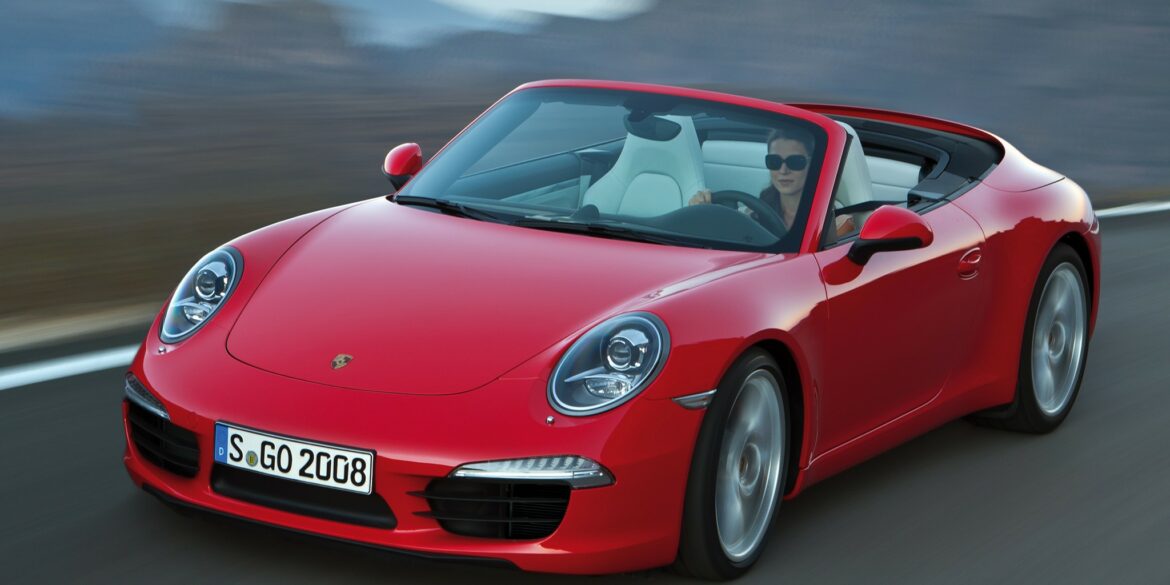
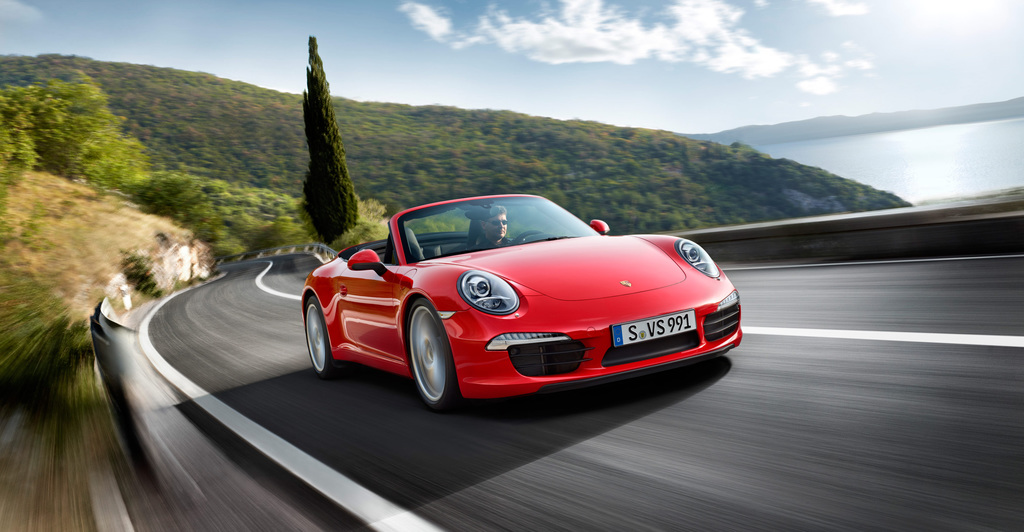
The 2014 Porsche 911 Turbo Cabriolet is a great companion to its coupe sibling. The Porsche 911 Turbo Cabriolet delivers the same blend of dynamism, performance and efficiency offered by the Coupe. The turbocharged 3.8-litre six-cylinder engine delivers 520 bhp and it helps drivers accelerate from zero to 60 mph in just 3.1 seconds (there goes your hair style). Compared to the 997.2 Turbo Cabriolet the new Turbo Cab delivers 30 bhp more power and are 0.2 seconds faster in terms of their standard acceleration. It is also up to 15% more efficient and more luxurious and comfortable to boot.
538 results for
997
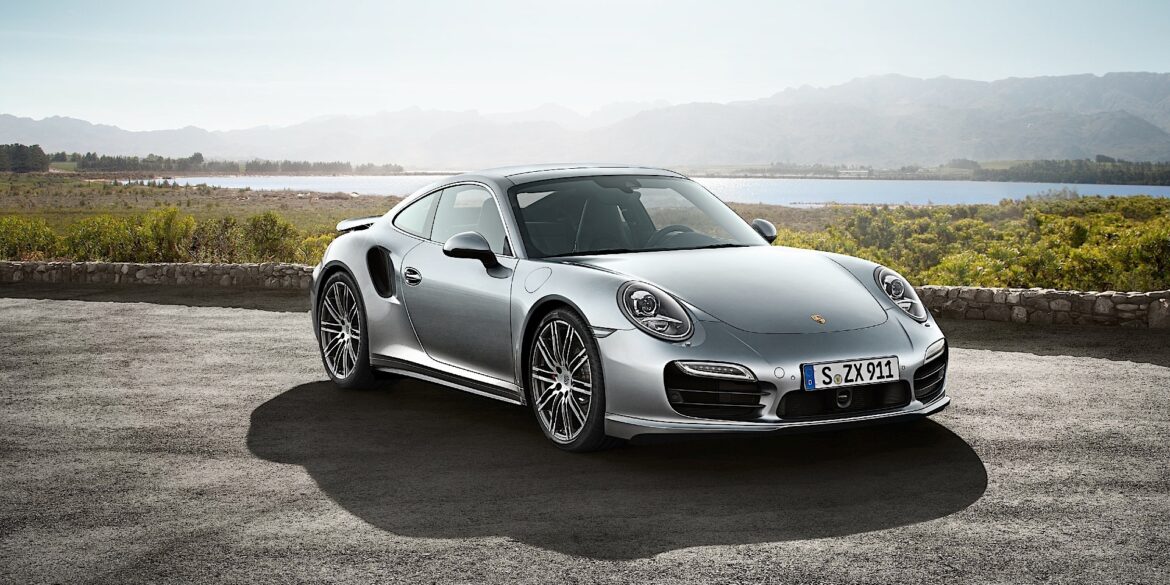
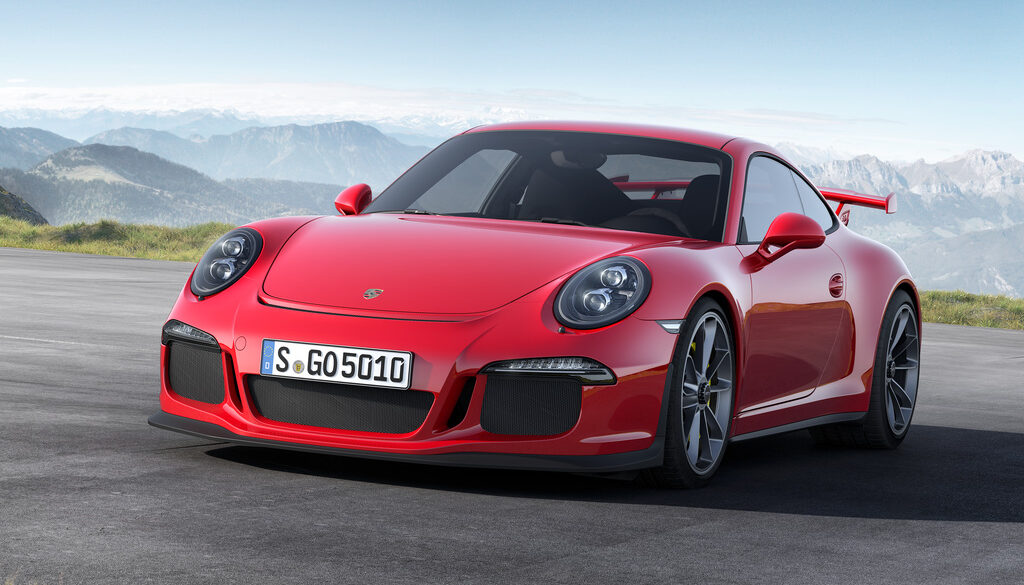
The 2014 Porsche 911 Turbo is a technological extravaganza. Adaptive aerodynamics, four-wheel steering, torque vectoring, active four-wheel drive, adaptive dampers, launch control, twin-clutch automatic gearbox – you get the picture. This is the first time we've had a chance to sample all of this on British roads. Two versions are available; both are powered by an uprated version of the previous 911 Turbo's 3.8-litre twin-turbo flat-six engine. The new 911 Turbo has even more power and more electronic systems. It is still a straight-line monster that will blow you away in terms of the sheer might of that engine and traction.
The 2012 Carrera 4S Cabriolet had the same wider rear track when compared to the non-S version of the vehicle. It wasn't something everyone would notice, but the difference was there for a reason, and that reason was the wider tires installed. From behind, a rear red light-strip united the LED taillights. Inside the Carrera 4S Cabriolet, there were some luxury features. The leather-covered sport-bucket seats were covered in leather. Even the rear, unusable, seats were wrapped in leather. The center console was higher to give a sense of a single-seat racing roadster.
The new all-wheel drive 911 is being launched on the market in four versions – as the 911 Carrera 4 and 911 Carrera 4S and each as Coupé and Cabriolet. The Coupé and Cabriolet of the 911 Carrera 4 S each have a 3.8-litre rear-mounted boxer engine that produces 400 hp (294 kW); this enables acceleration to 100 km/h in 4.1 seconds (Cabriolet: 4.3 seconds) and a top speed of 299 km/h (Cabriolet: 296 km/h) with a suitable equipment configuration. Fuel consumption values with PDK are 9.1 l/100 km (CO2 215 g/km) for the Coupé and 9.2 l/100 km (CO2 217 g/km) for the Cabriolet.
The new Porsche 911 Carrera 4 unites the excellent performance and efficiency of the new generation of the 911 Carrera with the dynamic benefits of the latest version of the active all-wheel drive system PTM (Porsche Traction Management). The typical Porsche all-wheel drive with rear-focused layout in this latest 911 version guarantees maximum vehicle dynamics on a wide variety of road surfaces and in all weather conditions. The new 911 Carrera 4 models deliver traction and dynamic performance the power of four.
The 2013 Porsche Carrera 4 featured a 3.4-liter flat-six engine. It was mated as standard to a world's first seven-speed manual transmission. An automatic, PDK (dual-clutch) transmission was offered as an option. The Carrera 4 featured an all-wheel-drive torque distribution in the instrument cluster display. The most distinctive identifying feature of the 911 with all-wheel drive is still the wide rear section: compared to the two-wheel drive 911 Carrera models, the rear wheel housings 22 mm wider, and each of the rear tires is 10 mm wider.
The open-top 991 Carrera S Cabriolet requires an $11,600 premium over a comparable coupe; ta not-cheap $108,950 price point for those shopping. For that, you get the best overall open-top sports car around. With the 400-hp, 3.8-liter six and the benefit of the PDK automatic’s launch control, the Carrera S cabriolet should hit 60 mph in 3.8 seconds and cover the quarter-mile in the low 12s. Performance is on-par with the coupe on backroads so any fears that this is a soft-911 are thrown out the window. This is a serious sports car, sans roof.
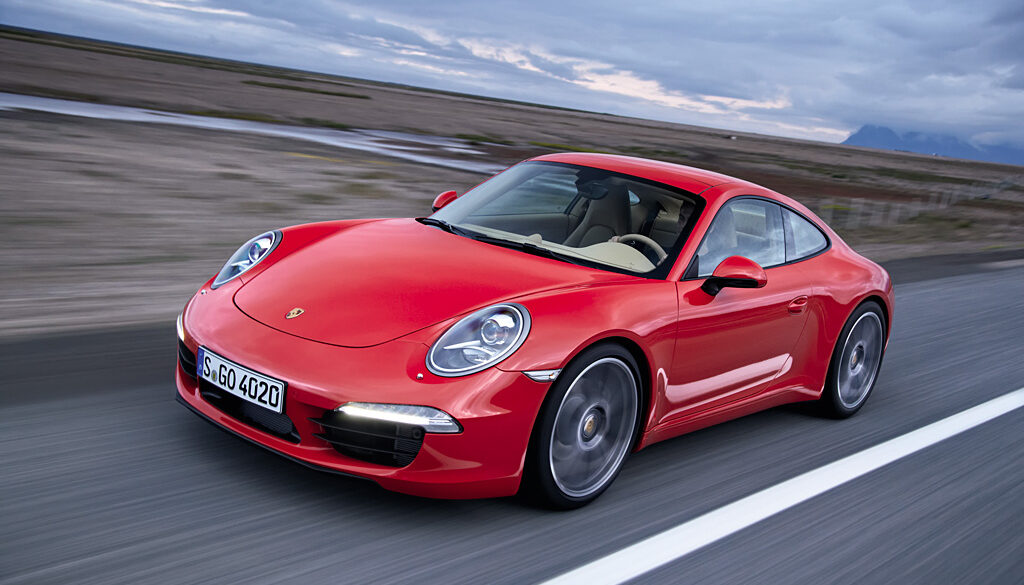
The 991 Carrera S continued the time honored Porsche 911 tradition of growing in physical size and power. Over the years the 911 has continued its evolution from a pure sports car to a luxurious super-car and the 2012 Carrera S Coupe was no exception. The seventh generation 911 launched in 2012 and it sits on a new platform, with a longer wheelbase and shorter overhangs. It also featured new headlights and taillights. Features a 3.8-liter flat-six engine mated as standard to a world's first seven-speed manual transmission.
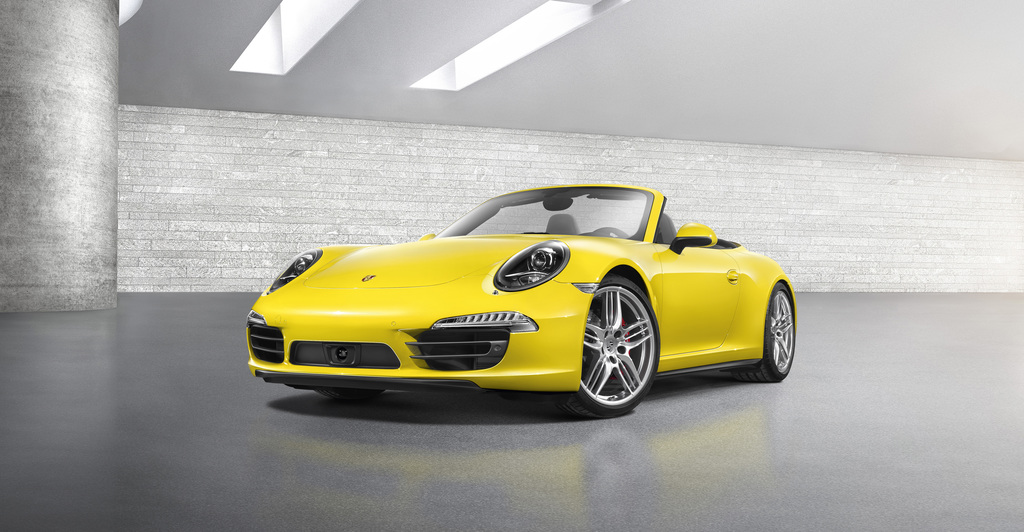
Porsche is doubling the driving fun to be had from the new 911 Carrera by putting a Cabriolet alongside the Coupé. The debut of the new generation of the sports car classic is being followed only a few months later by the open-top models of the 911 Carrera and 911 Carrera S in the new 911 design. What the Coupé began with the new aluminium-steel body, the Cabriolet continues with the all-new, unique hood: As a result, the typical 911 roof line is initially retained in its entirety.
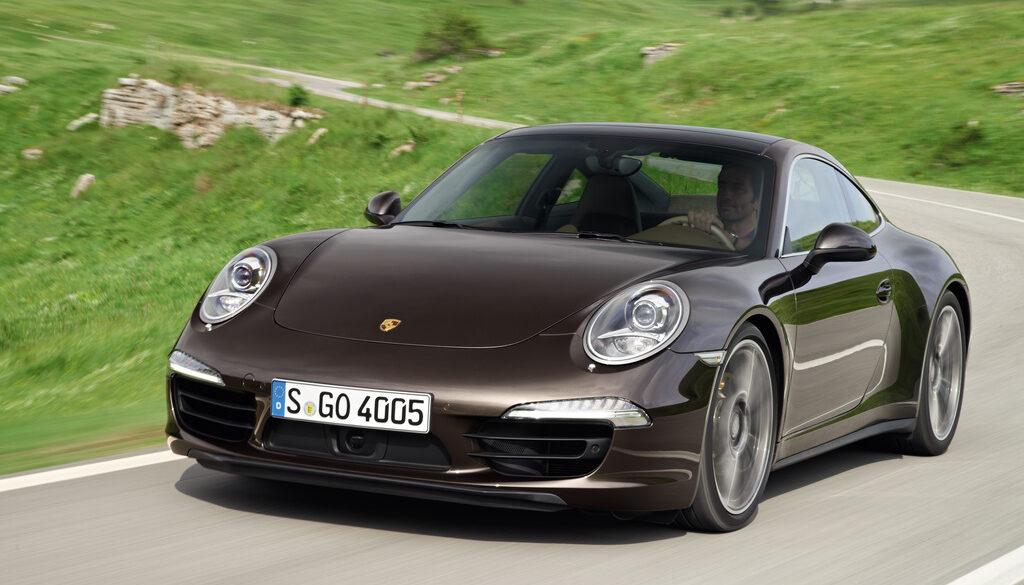
The seventh generation 911 was revealed 2011 Frankfurt Motor Show as an all-new model. It sports a longer wheel base, seven-speed gearbox and more efficient 3.4-liter flat-6. Major options include a 7-Speed automatic transmission , dynamic engine mounts and a Sport Chrono Package with a dash mounted analog stopwatch. This package also features a Sport Plus button that changes the settings of the chassis, engine and transmission for spirited driving. Launch Control is also new.
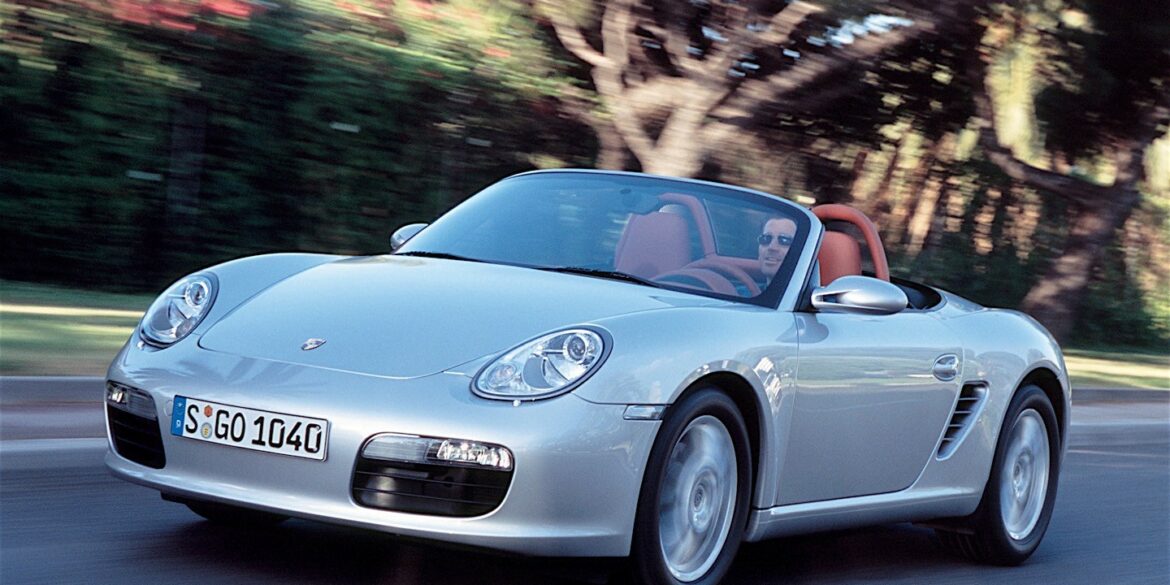
The original Porsche Boxster was a huge success and help Porsche grow its customer base, so when the second-generation Boxster (987) came to the US market as a 2005 model it wasn’t a surprise that it followed a similar formula. While the 987 Boxster retained only 20 per cent of the 986’s DNA, it looked similar enough to us that it felt more like a mild refresh than a totally new model update. The engine and transmissions were, for the most part, carry-overs, albeit with the obligatory and customary modest bump in performance and power (now at 240 horsepower).
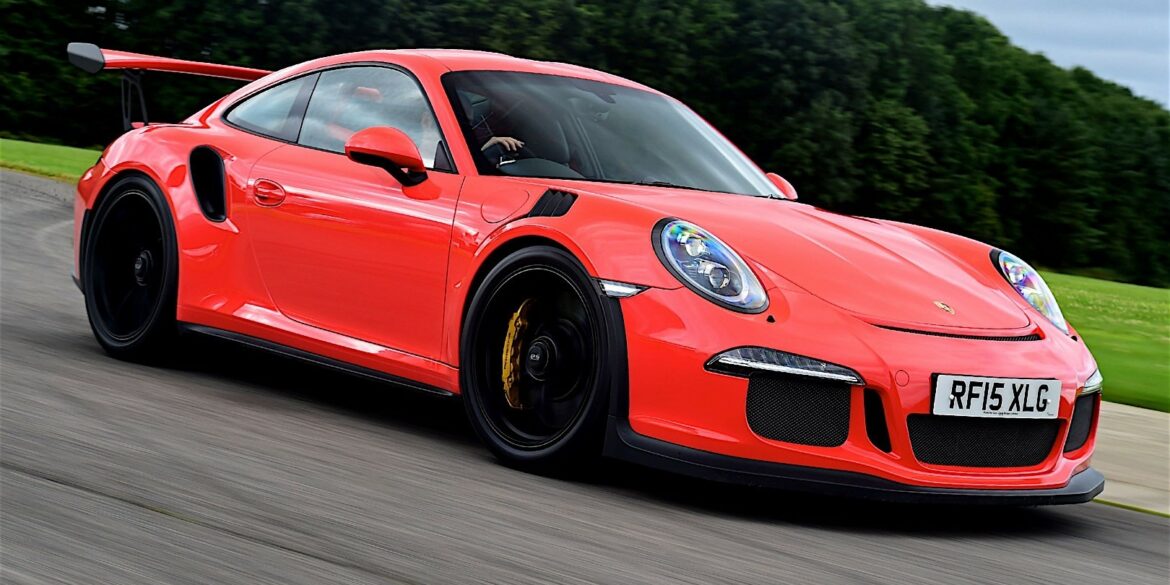
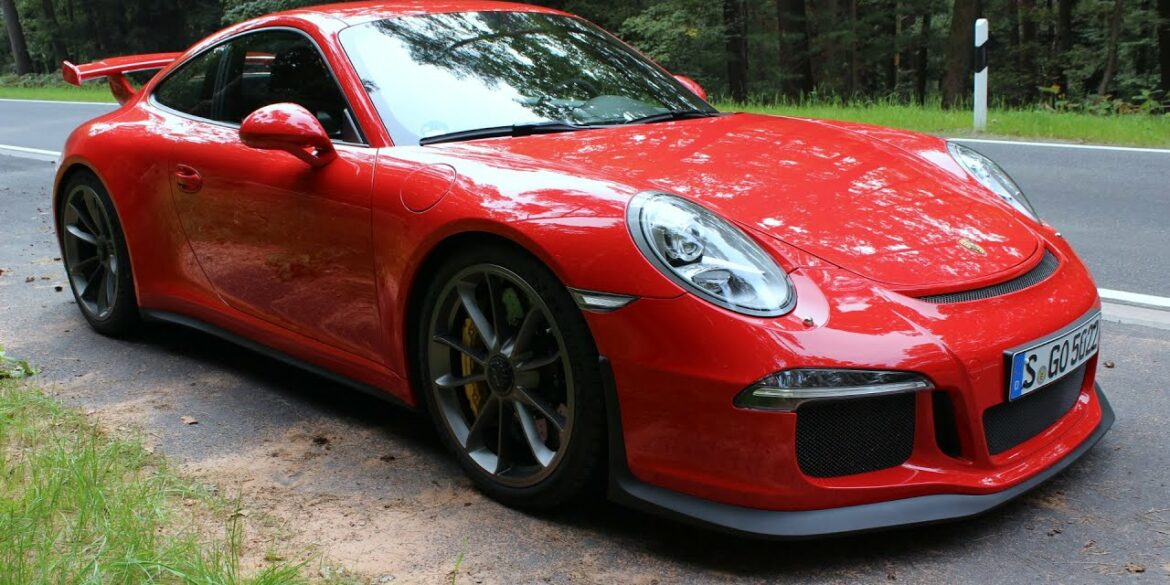
For those who want more extreme performance, handling and track-day bragging rights, the RS is it. It's far from practical and may be too extreme for some, especially on the street, but on track it is exceptional. Only marginally quicker than the 991 GT3 that it is based on, but it delivers that performance with a different character. Massive grip, massive downforce and more extreme than the GT3. It delivers 80 per cent of the downforce of the full-on GT3 R race car, and with a carbon fibre bonnet and wings, a magnesium roof and polycarbonate rear windows and screen, it’s also light, weighing in at just 1,420kg.
Porsche introduced the 991 GT3 for the 2014 model year, as follow up to the multiple 997 GT3 variants. The 991 GT3 featured a new 3.8 litre direct fuel injection (DFI) flat-six engine developing 475 hp (354 kW; 482 PS) at 8,250 rpm, Porsche's Doppelkupplung (PDK) double-clutch gearbox, and rear-wheel steering. The 911 GT3 is claimed to be able to accelerate from 0-60 mph (97 km/h) in 3.1 seconds or less, and the quarter mile in 11.2 seconds at 126 mph (203 km/h). It evolved into the 991.2 GT3 for model year 2018.
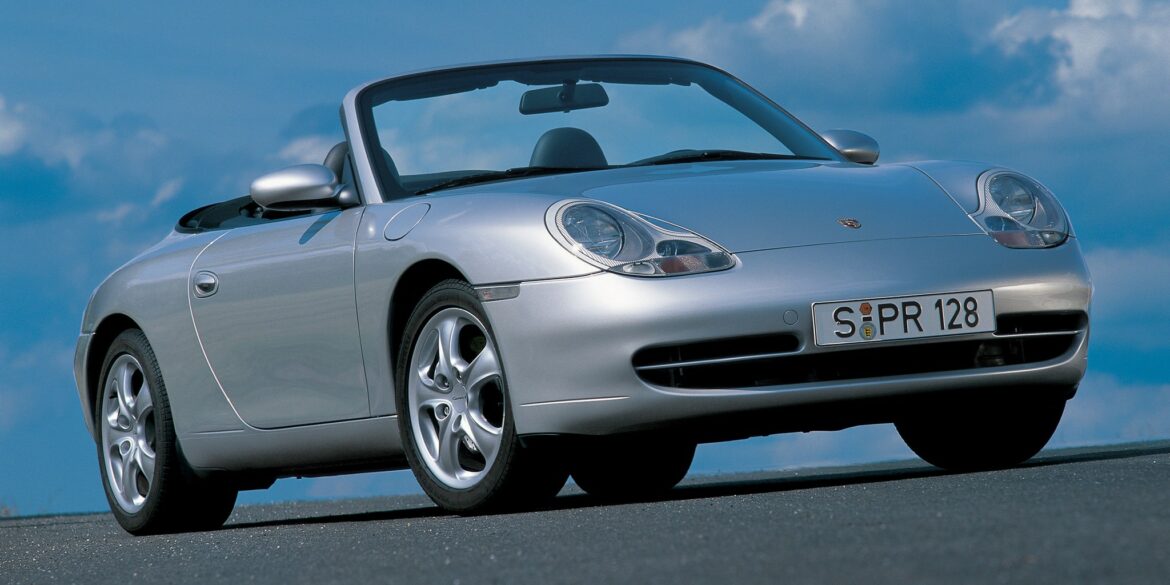
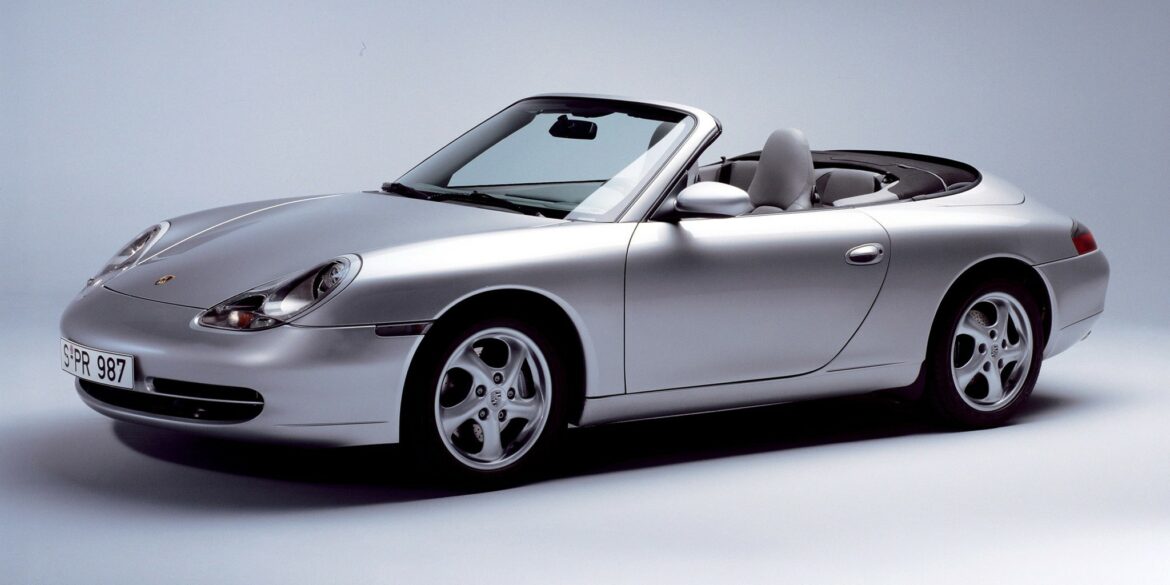
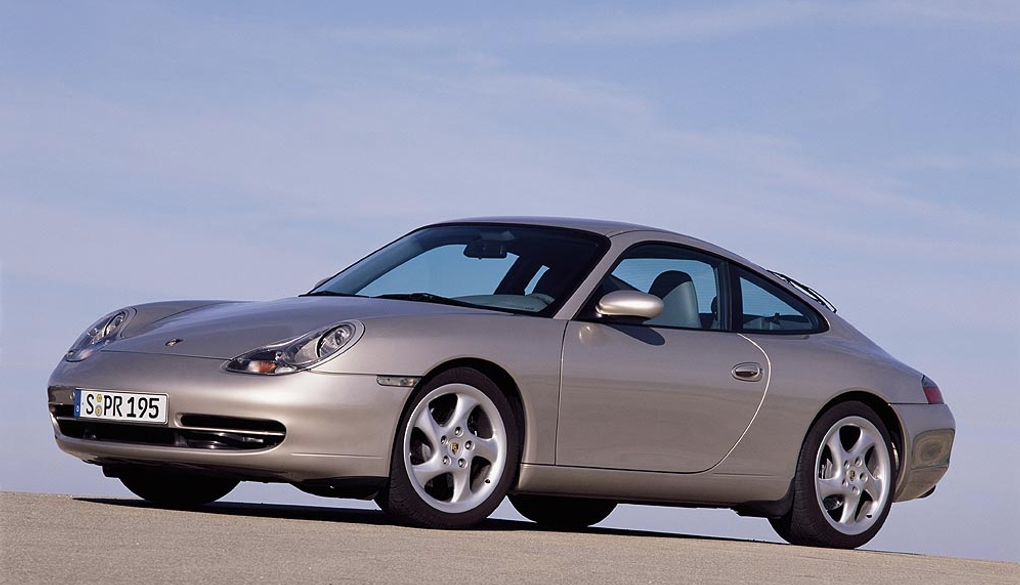
The 996 Cabriolet was introduced in March 1998 at the Geneva Motor Show. The 996 Cabriolet was long ready (remember, it was tested already in 1995), but for marketing and production-related reasons it was launched in 1998 as a 1999 model. While the evolution with the 911 coupe was questionable from 993 to 996, the real evolution came with the cabriolet. In USA - the biggest market - 911 Cabriolets outsold the Coupés. The all-wheel-drive system provides between 5-40% of torque to the front wheels depending on the situation.
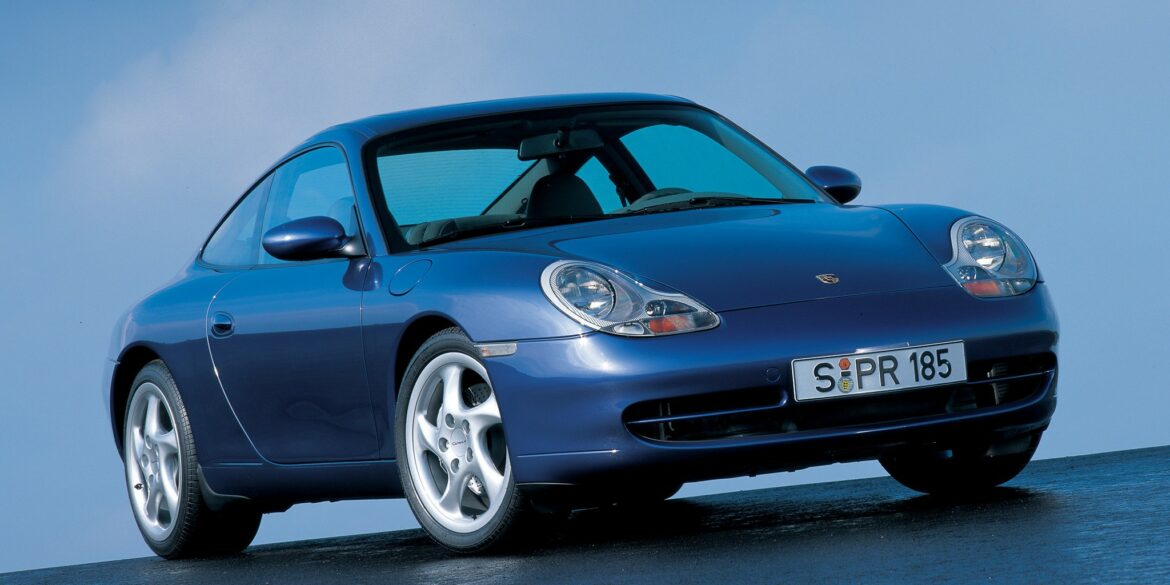
Since 1989, the rear-wheel-drive Carrera has always been accompanied by an all-wheel-drive Carrera 4, and the 996 was no different. Overlapping with the last year Carrera 993'S, the 996 Carrera 4 represented two major changes for the venerable 911 lineage: a water-cooled flat-6 engine replaced the air-cooled engine used in the previous 911 model, and the body shell received its first major re-design. Engine was 3.4 L and power was 296 hp featuring a change to an "integrated dry sump" design and variable valve timing.
The flat six in the Carrera 996 was a newly-developed flat-six engine that offered 300 hp. It was mated as standard with a six-speed manual. A 5-speed automatic (Tiptronic) with manual override to shift gears was on the options list. As always, the Carrera 2 was rear-wheel-drive. Designed as a grand tourer, the Porsche Carrera Cabriolet was the base version for the open-top 911 range in 1998. The retractable roof was able to be stowed away in 20 seconds at speeds of up to 50 kph (31 mph), like the rest of the 911 convertible range. With the roof up, the car was tested in the wind tunnel at speeds of up to 338 kph (210 mph).
The 996 series was a monumental update to the 911 story. The Type 996 introduced water-cooled engines and it also ushered in a new body design. The roof line with a windscreen which is around five degrees flatter gives the side view a more fluid look. Gone was the "classic" 911 design, the entire main body now much sleeker. The flat six in the Carrera 996 was a newly-developed flat-six engine that offered 300 hp. It was mated as standard with a six-speed manual. A 5-speed automatic (Tiptronic) with manual override to shift gears was on the options list. As always, the Carrera 2 was rear-wheel-drive.
TheGetawayer Reviews the 991.1 GT3 I finally review the new 2014 Porsche 911 GT3 (991). Can it match the driving experience of the old 997 GT3 and does it still feel like a proper GT3 ? Here are my in-depth impressions.....
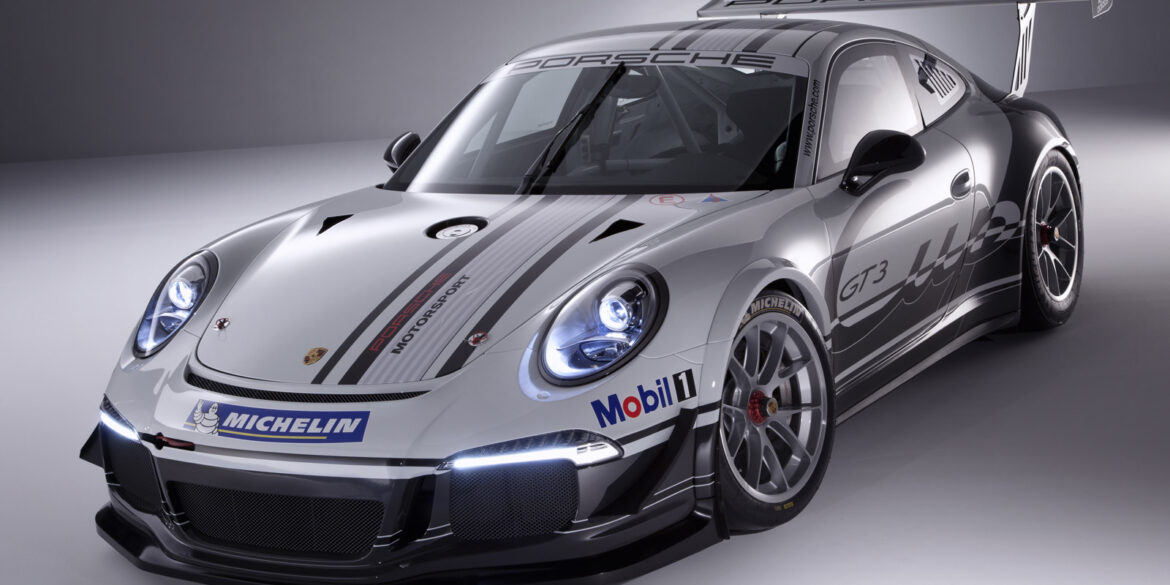
The new Porsche 911 GT3 Cup is powered by a 3.8-litre six-cylinder flat engine. It generates 460 hp (338 kW) at 7,500 revs, surpassing the predecessor by 10 hp. A six-speed dog-type gearbox developed by Porsche Motorsport which is operated via shift paddles at the steering wheel for the first time in a Porsche brand trophy race car transmits the power to the rear axle. The single piece race wheels with centre mount were also new.
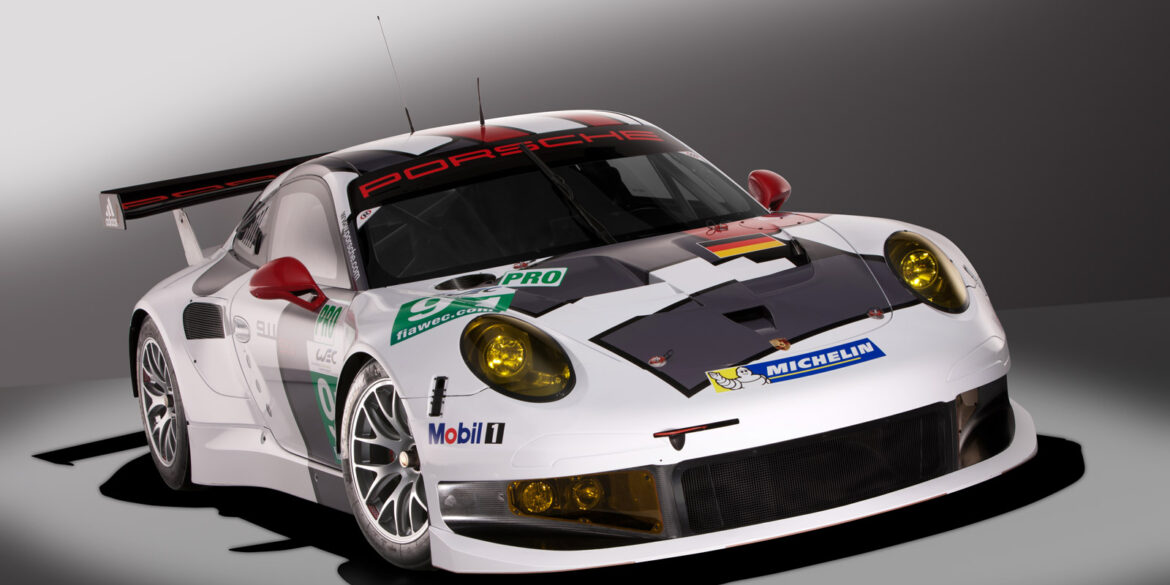
As the rules do not permit higher output engines, the engine for the 991 RSR was taken from the 997 GT3 RSR 4.0 and the development work focused on the chassis, body, aerodynamics and the gearbox. A wishbone front suspension replaced the McPherson struts used in 997. A new development was the lightweight gearbox. One of the priorities in the development was the more evenly balanced weight distribution. The centre of gravity was lower, too.
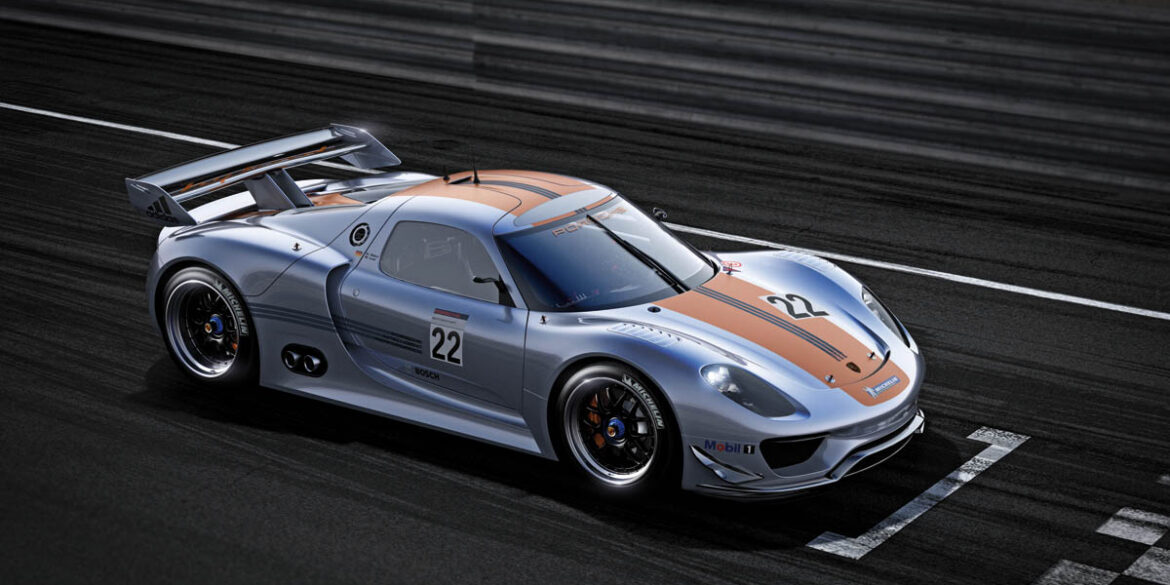
Porsche 918 Spyder Prototype is a combo of mis-matched Porsche parts that looks more like a Frankenstein car than a cutting edge technical automotive marvel. But don't let the crazy exterior fool you because underneath, the 918 Spyder Prototyp is a pure science experiment designed to wow us in a few years.
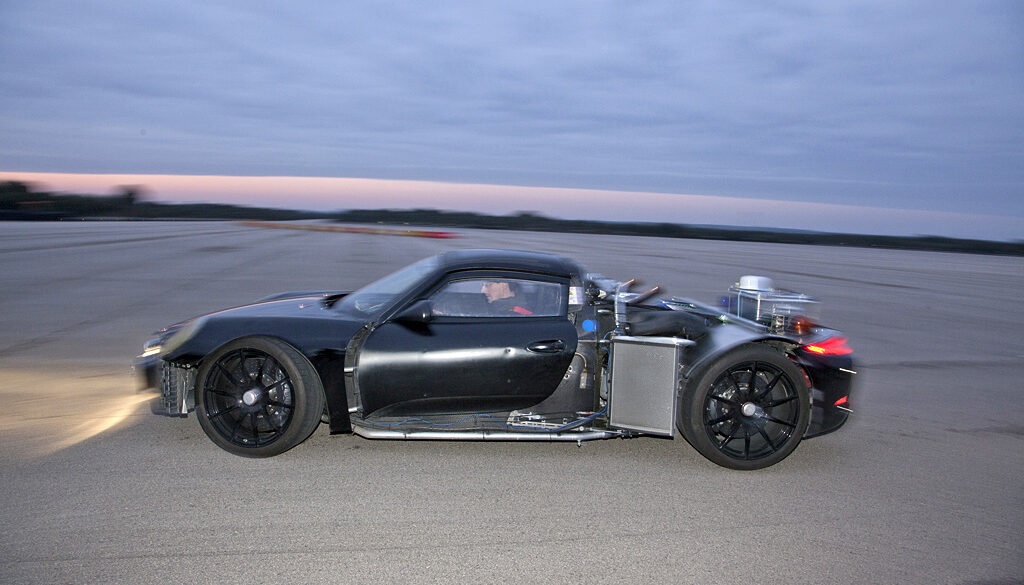
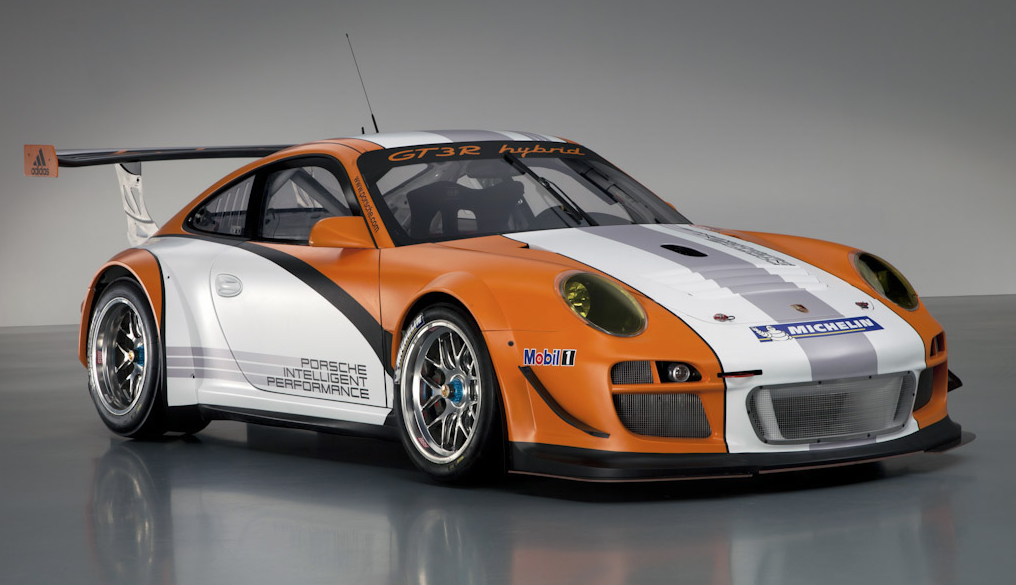
The Porsche 997 GT3 R Hybrid 2.0 is an update to the 997 GT3 R Hybrid. Compared to its predecessor, which debuted in 2010, the 2011 second-generation hybrid is 20 percent lighter and more efficient without any concession to lap times. While sharing the same paint scheme, the new vehicle is easily identified by its lack of intakes in front of each rear wheel - changes to engine cooling allowed the slats to be dropped and aerodynamic efficiency improved. It gets a traditional race-bred flat six engine. The GT3 R Hybrid has a completely independent second driveline in the front of the chassis, a clever and complex hybrid electric set up that rockets it from standstill to 60 mph in just 2.5 seconds.
Made as a demonstrative show-car, the 918 RSR ‘Racing Lab’ was part of a new initiative called Porsche Intelligent Performance which will likely develop hybrid racing cars for outright victories at events like the 24 Hours of Le Mans. The concept version revealed at Detroit has the same visual styling cues as the Spyder released in 2010 with the hybrid drive system from the 911 GT3 R Hybrid.
Autocar Compares the BMW M3 GTS to the 997 Porsche 911 GT3 Can the hardcore BMW M3 match the legendary Porsche 911 GT3’s poise? See the two track-biased sports cars go head to head....
Auto Express Reviews The 997 Porsche 911 GT2 RS The 911 GT2 RS is the fastest and most powerful production car the company has ever made, and only 500 examples will be built. It’s the ultimate expression of the 911’s sporting ability, and the carbon fibre bonnet and polycarbonate windows...
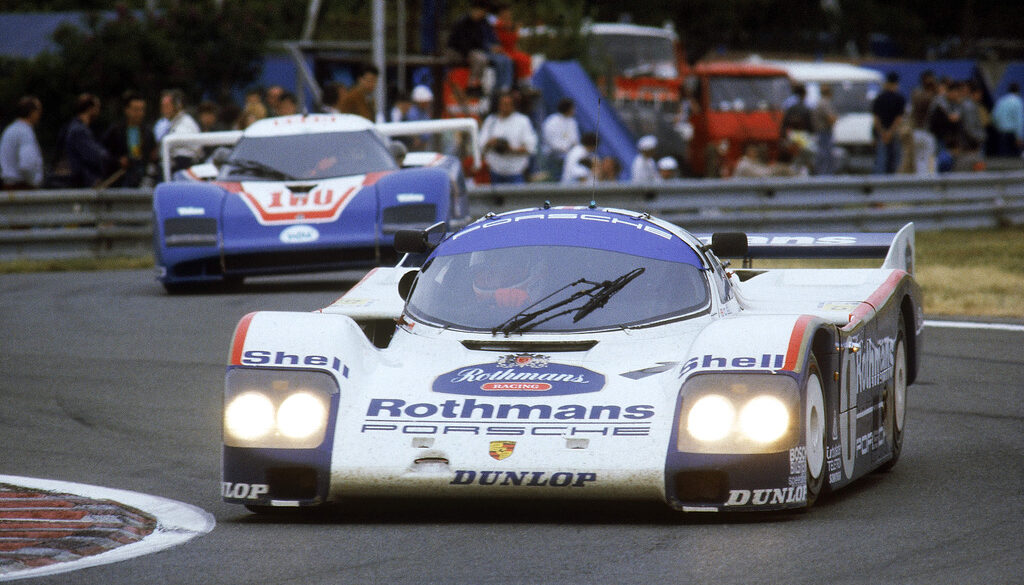
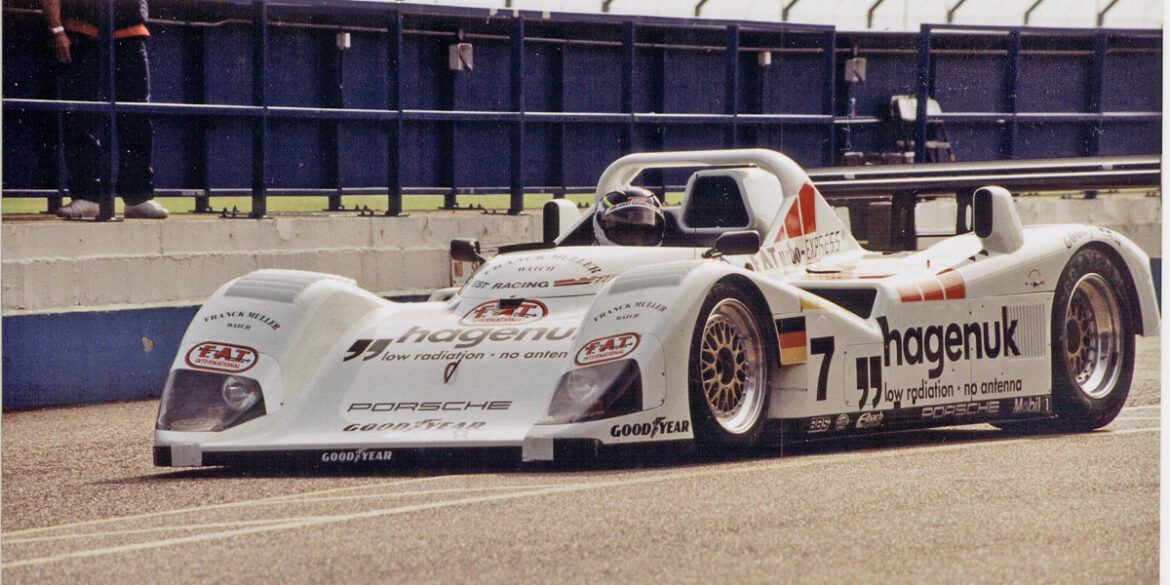
The Porsche WSC-95 (sometimes referred to as the TWR WSC-95) was a Le Mans Prototype originally built by Tom Walkinshaw Racing. It was modified by Porsche from the original Group C Jaguar XJR-14 from which it derived,[1] and run by Joest Racing. The WSC-95 saw very little race action even though it won the 24 Hours of Le Mans in both 1996 and 1997 without being acknowledged as a factory supported project. Later upgraded to the Porsche LMP1-98 before being retired. Only two cars were ever built.
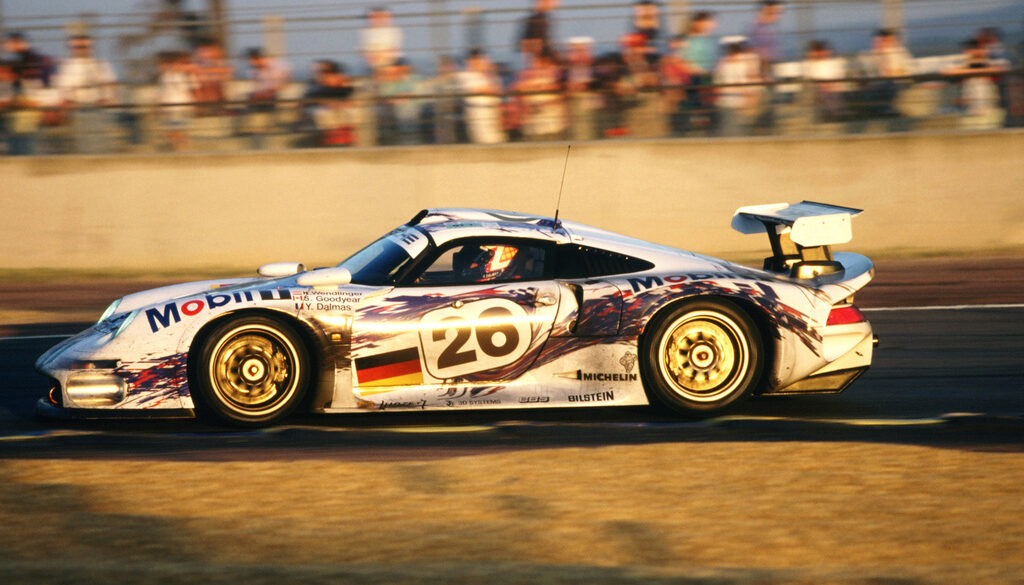
In spite of its 911 moniker, the car actually had very little in common with the 911 of the time, only sharing the front and rear headlamps with the production sports car. Designed and developed to compete in the GT1 class of sportscar racing, which also required a street-legal version for homologation purposes. It was powered by a twin-turbo flat 6 that was good for 600 bhp. The 1996 911 GT1 clocked at a top speed of exactly 330 km/h (205 mph) on the legendary Mulsanne Straight.
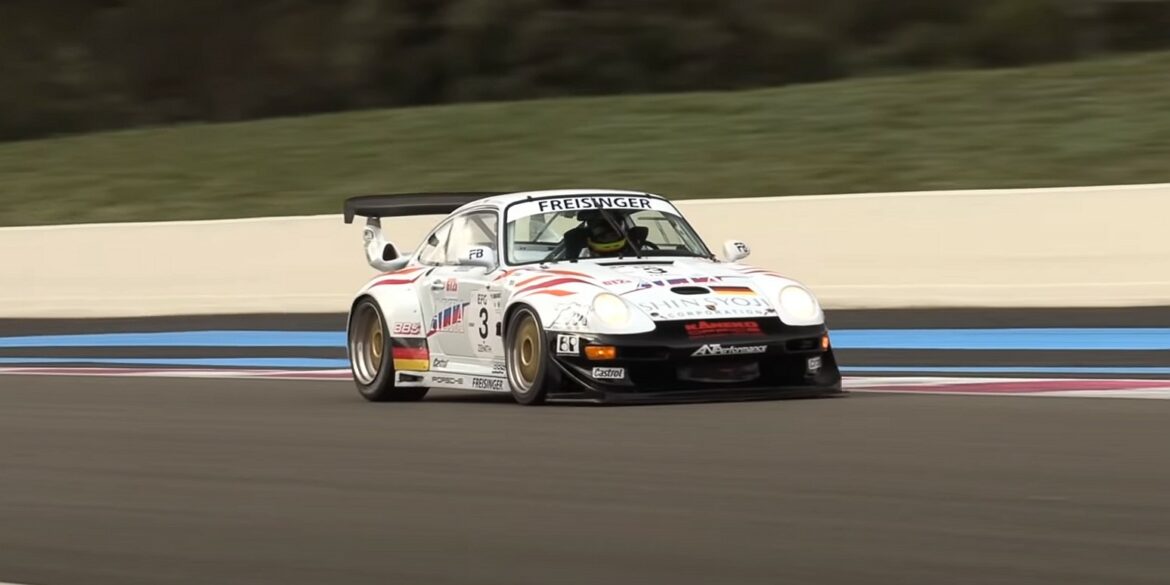
The racing sportscar is prepared by Porsche following the Le Mans GT2 regulations for the over 1,150 kg weight classification. It features a 3.6-litre engine with two turbo-chargers (KKK 24 with 33.8 mm restrictors), which delivers around 450 hp at 5,750 rpm. Even this racing vehicle, with its suspension featuring a McPherson front axle and Porsche multi-link rear axle with LSA system, closely resembles its production relative. Utilizing a steel 993 Twin Turbo chassis with modifications for racing, scored numerous victories in a wide variety of racing venues.
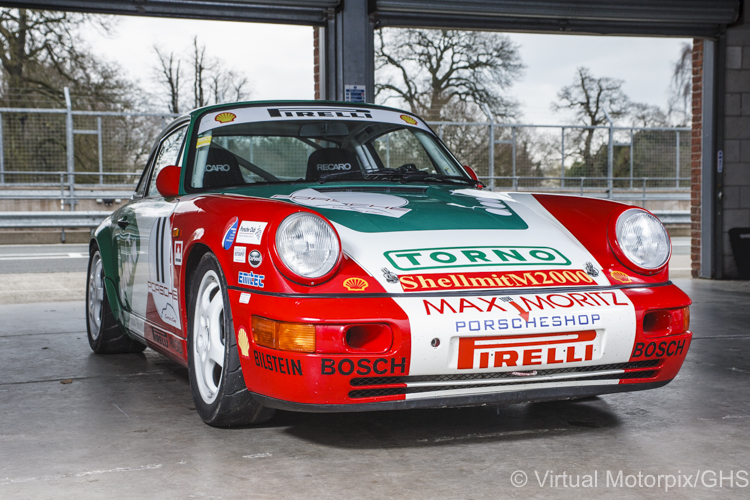
Introduced in 1989 (the year of the 911’s 25th anniversary), the 964 Carrera 4 was a significant new model for the company, but the 4-wheel drive system was deemed unsuitable for the company’s racing series. Manufactured alongside the Carrera 4 at the same time was the more traditional rear-wheel drive Carrera 2, but this model’s launch was only planned for a year later, in the hope that it would not detract from potential sales of the Carrera 4. The 1990 season was the first season that saw the 911-based model become the pillar on which the Porsche Carrera Cup series has been established.
The Porsche 962 arrived on scene in 1984 as essentially a Porsche 956 for the IMSA/US market. A biturbo version was used in competition racing in Europe, while an IMSA version with a turbocharger featured in North America. The 962 C was based on the 956, with a 120 millimetre longer wheelbase and competed in LeMans. It differed from the IMSA version. The driver trio Stuck/Bell/Holbert was victorious at Le Mans in 1987. Porsche offered the 962 to privateers to race on their own and they were hugely successful.
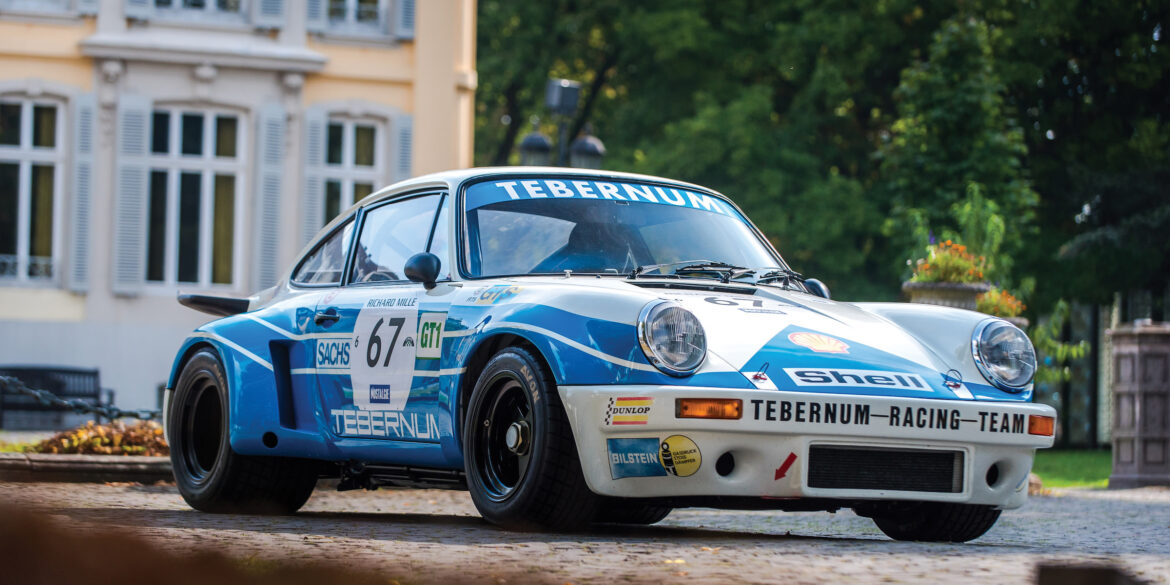
For the 1974 racing season 911 Carrera RSR 3.0 (246 kW) and RSR Turbo 2.1 (338+ kW) were created - the 3.0L for the customer teams and the 2.1 turbo for Porsche’s own team. The Carrera RSR 3.0 was made in small numbers for racing. The 3.0 RSR would go on to become the most successful Group 4 racing car of its time thanks to its combination of low weight, immense Porsche 917 brakes, impeccable handling, and a 330+hp naturally aspirated flat-6.
Introduced in 1973, the RSR was a factory-built racing car based on the 911 chassis. The Porsche 911 Carrera RSR 2.8 was the first 911 to ever wear the RSR badge. Homologated for racing by the iconic 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RS, the RSR’s racing career got off to the perfect start thanks to Brumos Racing’s overall triumph in the 1973 24 Hours of Daytona, while a factory car won the latest ever Targa Florio road race. For the privateer in the mid-1970s who wanted to go sports car racing this was the chosen weapon.
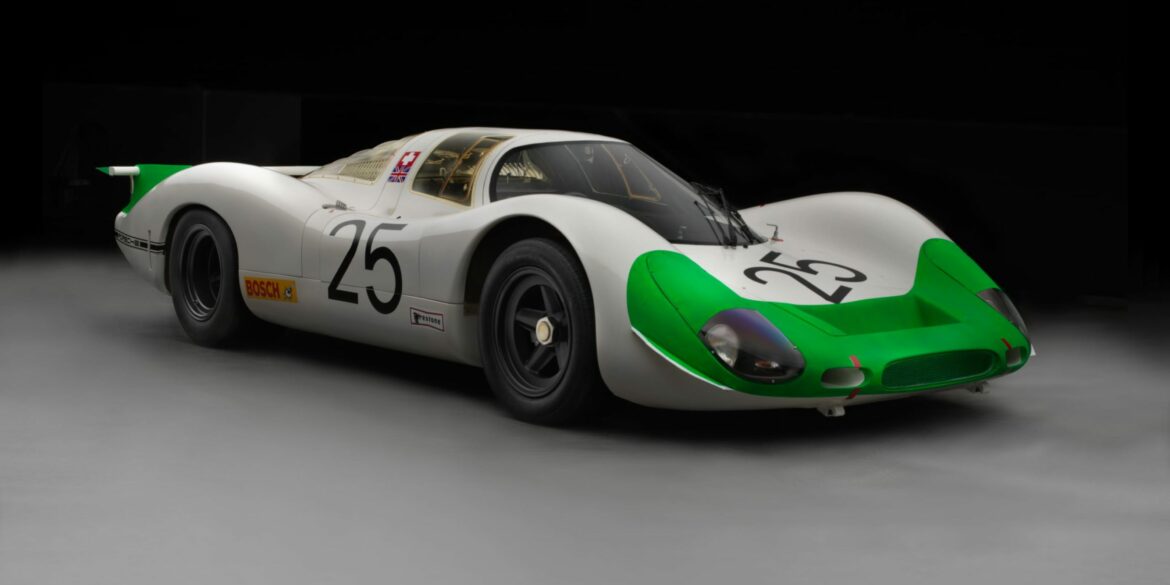
The longer tail 908 Spyders were created only with the Flunder body - the body that's upper surface is almost flat between the axles - and not with the "normal" curvy Spyder body. Very few LH Flunders were created, both with 908/02 and 908/01 chassis numbers. 908 LH Flunder Spyder was first used at the 1969 Le Mans 24h race by Jo Siffert and Brian Redman, but they had to retire because of the gearbox failure. The only excellent result was 3rda at the 1970 Le Mans.
The 908/02 K Spyder and 908 K Flunder Spyder were basically the same cars with slightly different bodyworks. If you look at the non-Flunder Spyder, you see that the body drops after the front wheel arch and rises again before the rear wheel arch. In the Flunder version, this concavity doesn't exist. The difference between the two versions was mainly visual, no difference in racing use. The first competition the Flunder was entered, was the Nürburgring 1000 km on June 1, 1969.
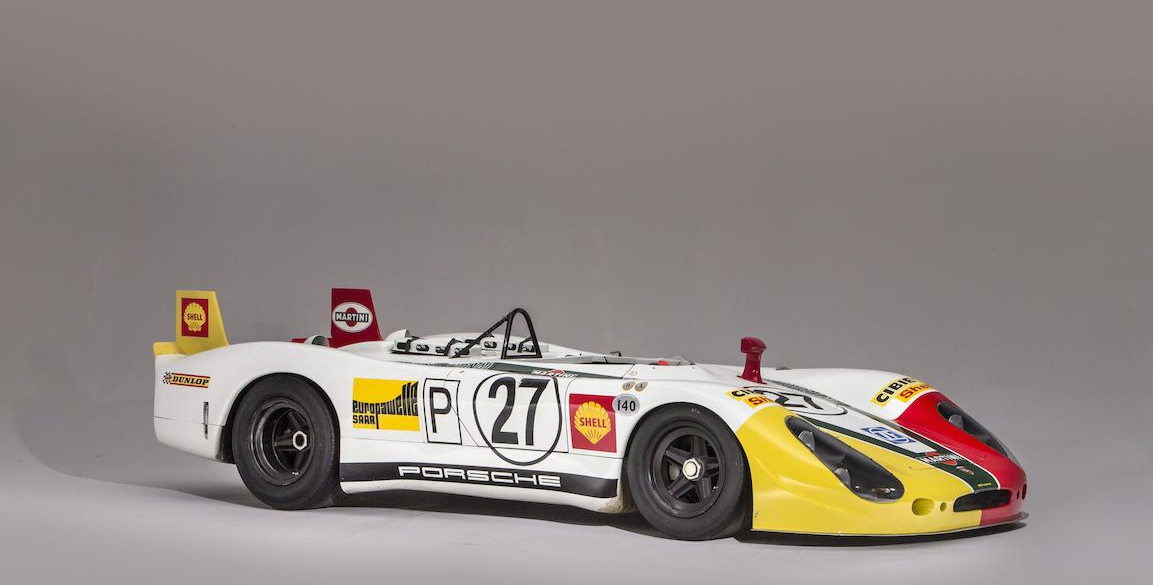
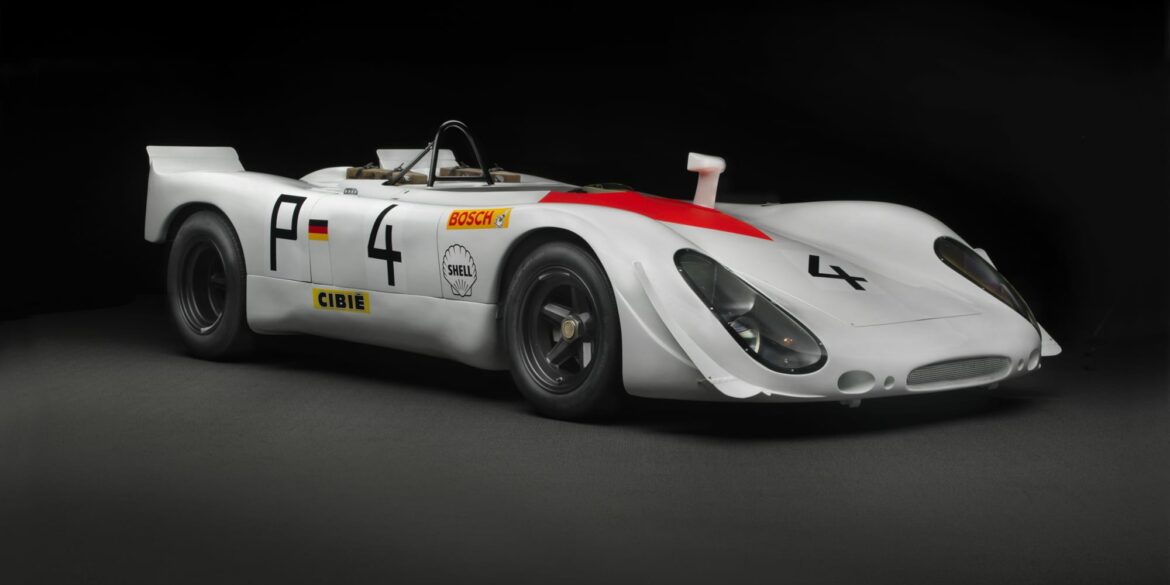
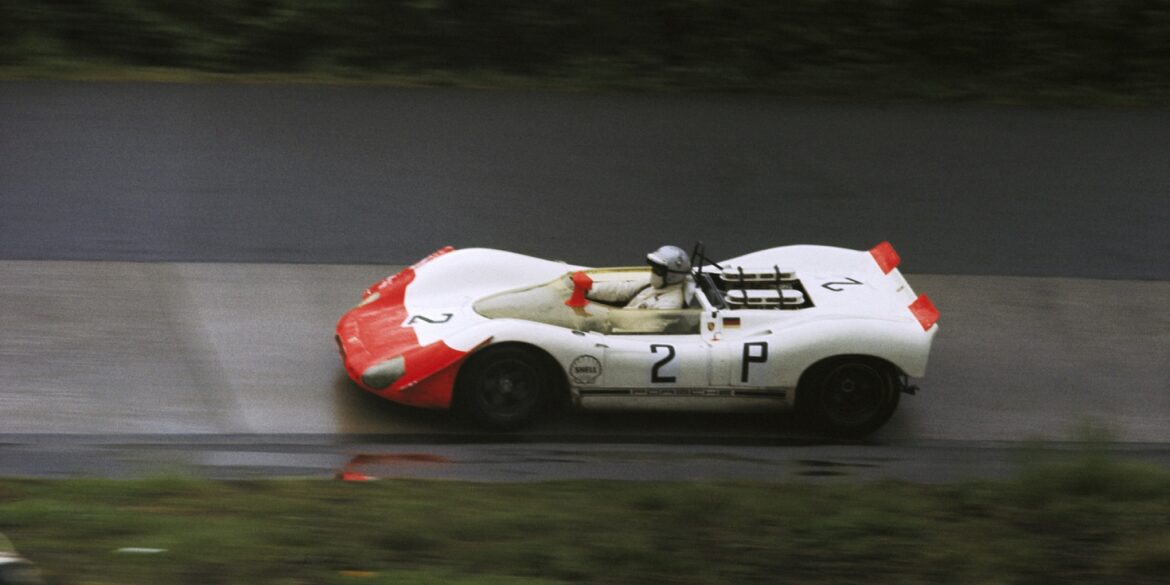
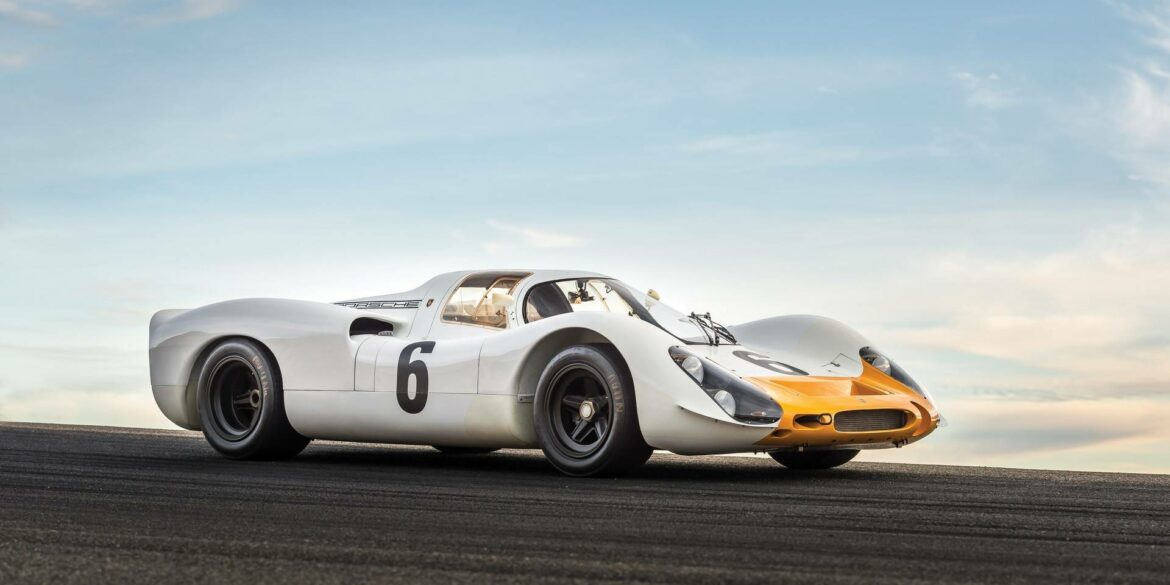
Introduced in 1969, the three-litre 908/2 is an evolution of the Porsche 908K Coupe. As the rule book for the season no longer required a minimum windscreen height nor the requirement to run a spare wheel, Porsche opted for a much lighter Spyder body; which looked like a chopped version of the short-tail Coupe used in 1968. The Spyder body was perfectly suited for high downforce races like the Nürburgring 1000 km and the Targa Florio. It was also about 100 kg lighter than the Coupe.
The Porsche 908/01 K Coupé was basically a 907 K with the new 3-litre flat-8. “K” in the designation stands for Kurz which is “short” in German, meaning the car had short-tail body compared to the 908 LH (“langheck”, long-tail). Although 907 and 908 were similar, there was a visual difference - the 907 had symmetrical front openings and the 908/01 K had asymmetrical. The 908/01 K debuted on May 19 at the Nürburgring 1000 km race and won it outright.
The FIA’s new three-liter prototype (Group 6) and five-liter sports car (Group 4) regulations adopted for 1968 presented the opportunity for Porsche to update its 907, which had won races but lost the championship. In came a 2997 cc flat-eight engined 908. Despite its aero appearance, it was no easy car to drive fast, weaving as speeds approached 200 mph. Despite winning the 1000km Nürburgring, the 908 was anything but convincing in 1968.
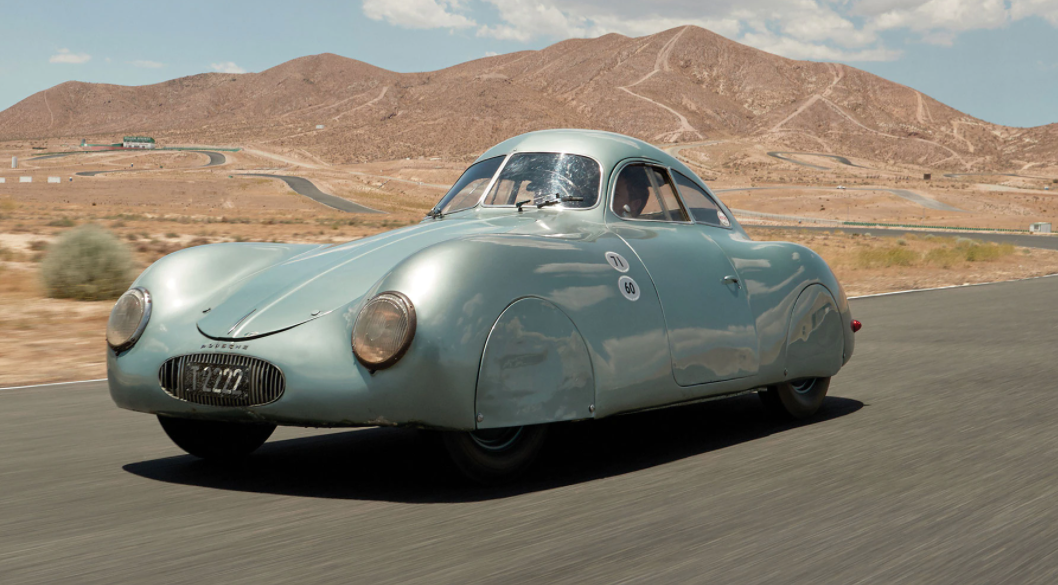
The Porsche 64, also known as the Type 64 and Type 60K10, is considered by many to be the first automobile from what was to become the Porsche company. The first KdF Berlin-Rome competition car, chassis number 38/41, was finished on August 19, 1939. It had a streamlined body and small 4-cylinder aircooled 1100 cc flat engine.
No More Content