Porsche 911 GT3 RSR (996) (2004 – 2005)
For the 2004 and 2005 racing season, Porsche Motorsport used the 911 GT3 RSR. This near-standard racing sportscar aimed to keep private customer teams competitive.
For the 2004 and 2005 racing season, Porsche Motorsport used the 911 GT3 RSR. This near-standard racing sportscar aimed to keep private customer teams competitive.
Modeled on the 911 GT3 R, the GT3 RS race cars offered a number of technical improvements
In the 2000 FIA GT Championship, the 996 GT3 R was the dominant racer in the new N-GT class and won every run.
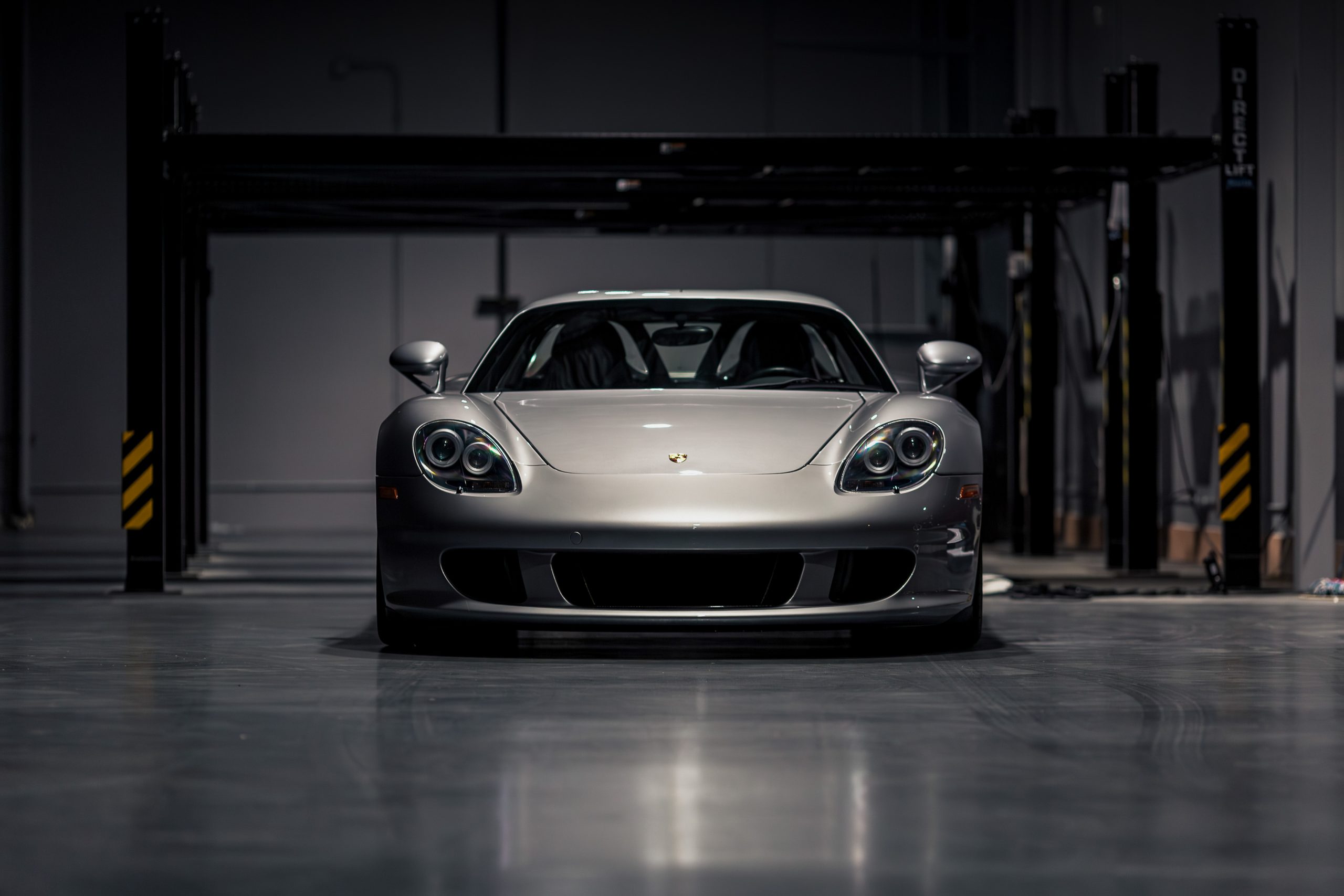
The Porsche 9R3 was meant to address Audi's Le Mans dominance. Instead, it gave its V10 heart to the Carrera GT.
Built for racing, the 996 GT3 Cup served as the basis for the 996 GT3 road car.
The Porsche WSC-95 was a Le Mans Prototype originally built by Tom Walkinshaw Racing. It was later upgraded to the Porsche LMP1-98 before being retired. Only two cars were ever built.
The Porsche 911 GT1/98 – Winning Le Mans in 1998
Towards the end of the 1996 season, Porsche made revisions to the 911 GT1 in preparation for the 1997 season.
Designed and developed to compete in the GT1 class of sportscar racing. Good for 205 mph...
Combined the RSR’s purity of purpose with a tuned version of the 993 Turbo’s twin-turbo engine
Developed at Porsche’s race department using the platform of their new 993 Carrera 2
An all-out racing car. The RSR 3.8 could be delivered to the track in a race-ready, ‘just-add-driver’ form.
In 1992, Porsche introduced the 968 Turbo RS racecar which it developed to compete in the new ADAC GT racing series in Germany.
For race teams and track day customers Porsche prepared a small number of the 964 Cup cars according to the FIA NG-T regulations.
1987 - 1988. Unlucky and Unprepared Porsche CART Race Car
The greatest version of the 959 is, and always will be, the Rothman's liveried Paris-Dakar racing version.
The Porsche 961 was the racing version of the 959 supercar.
The Porsche 953 ranks as one of the finest off-roaders Porsche has ever made.
Built so that the factory Rothmans Porsche Rally Team could hit the international stage
Built by Porsche in 1982 for the FIA World Sportscar Championship. In 1983, driven by Stefan Bellof, this car established a record that would stand for 35 year
Röhrl's one-off drive at the 1981 San Remo Rally is regarded as one of the greatest drives ever
The ultimate development of the 924 in its race trim was the 924 Carrera GTR race car
These cars were designed by the factory to race in SCCA D Production Championship starting in 1979.
In 1978 a pair of 911s were entered into the East African Safari Rally.
The 935/78 was the ultimate expression of the 911 factory race car before Porsche officially withdrew from motor sport.
The Group 4 racer based on the 911 Turbo (930)
The Group 4 racer based on the 911 Turbo (930)
The Porsche 934/5 was effectively a hybrid of the Porsche 934 and 935 built to compete in Group 4 of the IMSA
Using the 930 Turbo as a basis, Porsche built the 934 for Group 4 GT racing.
Porsche decided to end its 20-year history of factory sports car racing and sold the 908/03 cars to customers. In 1975, some 908s were fitted with turbocharged engines.
The 3.0 RSR was one of the most successful Group 4 racing cars ever
The first turbocharged Porsche 911, and the first turbo-powered Porsche race car at Le Mans.
The first 911 to ever wear the RSR badge and homologated for racing by the 1973 911 Carrera RS
The 917/20 Turbo is a confusing car - its chassis number reads 917/30-001, but it is not the real 917/30
The Car That Killed Can-Am
The first turbo-Porsche, Can-Am winner 1972, Interserie winner 1972, 1973
The 1972 917/10 was similar to the 908/03, but had the 12-cylinder engine instead of the 3-litre flat-8.
Only two 917/10 were created in 1971.
The Pink Pig
For the 1971 Season, the 917 Kurzheck Coupé (917K) was upgraded in several ways
Like the 917 LH of 1969 and 1970, the 1971 version was also made for one race only - the 24 hours of Le Mans.
Built to take full advantage of new FIA rules allowing a two-inch wider track.
The 917 Kurzheck Coupé (917K) first appeared in 1970. A winner from day one.
Of all the 917 variants, the ‘Interserie Spyder’ was one of the most successful. It won the Interserie championship outright for two years in a row before the model was replaced by the 917/10 of 1972
The short tail 917 K ("Kurz" in German for short) was raced first. The only engine available in 1969 was the 4.5-litre flat 12.
For the 1969 racing season the absolutely new Porsche 917 with 4.5-litre 12-cylinder engine was created.
This 908 received a completely new tubular frame based on that of the 909 Bergspyder and its three liter engine was moved forward.
There was a belief that longer bodies are more aerodynamic and are therefore better for faster tracks, so a 908 Flunder Spyder with a longer tail was created
The 908/02 K Spyder and 908 K Flunder Spyder were basically the same cars with slightly different bodywork
Notching up over 50 major victories and more than 100 podium results, the 908/02 Spyder is one of the most successful Porsche race cars
The 911T in 1968 was the lightest 911 making it ideal for racing where the SWB T was homologated for Group 3.
In the late sixties, Ferdinand Piëch wanted Porsche at the top of motor sports and the 908 was his answer.
In the late sixties, Ferdinand Piëch wanted Porsche at the top of motor sports and the 908 was his answer.
The 909 Bergspyder did not win a major event. It ended up being an awesome laboratory of ideas (not all worked).
A lightweight racer designed to take the newly released 911 to its limit
The First Porsche Ever to Win a 24-Hour Endurance Race.
The 907 was conceived and built as a way to win the 1967 Le Mans race.
Porsche 910 was the evolution of the 906 with Ferdinand Piëch as its main driving force and Hans Mezger
In 1967 and 1968, Porsche's lightweight 910 Bergspyder was a championship-winning machine
Nine factory vehicles received the 2-liter, six-cylinder boxer engine with an injection system
Developed for endurance sports car racing, the 906 was a street-legal racing car that raced in the FIA's Group 4 class
Another four factory 906s received an air-cooled eight-cylinder boxer engine of the type 771, which was already used in the 904/8.
For the 1966 Le Mans 24h race, long-tail LH ("Langheck") versions were made and now the standard 906 were called as 906 K ("Kurz", short in German)
The 906 Spyder was the first Porsche racing car built under Ferdinand Piëch's orders and there could be only a person as determined as Piëch to use Lotus parts on a Porsche.
Three factory 904 race cars were fitted with a flat eight-cylinder power plant derived from the 1962 804 F1 car
Porsche's Attempt At Creating The Chinese People's Car
In 1965, the 904’s second and final production year, some examples received a version of the 911’s 2.0-liter flat-six. This version was dubbed the 904/6.
A four door performance sedan concept that maintained the iconic shape of the 911 Carrera
The Porsche 904 debuted late in 1963, for the 1964 racing season. The 1965 Porsche 904 Carrera GTS variant to compete in the FIA-GT class
After a long absence of a Carrera model in the 356 model lineup, Porsche made another version with the intro of a 2.0L engine.
When Dr. Ferry Porsche turned 80 years old, he received a 1989 Porsche Panamericana concept car as a gift.
The Porsche 804 competed in Formula One (F1) in 1962. Porsche developed an 8-cylinder engine for it.
Intended as the successor to the Porsche 930, the car did not get past the prototype stage.
In 1987 Porsche experimented with a long-wheel-base 928 called the H50
The Porsche Junior concept car.
The Porsche 965 was a V8-powered 911 from 1984
The 1961 Porsche RS was one of the last Spyders made by Porsche that used the potent 4-cam engine. It was a successor to the 1960 RS60
For the 1961 F1 season Porsche created a new car called 787.